* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Speech Operated Mobile Platform
Survey
Document related concepts
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Intermittent energy source wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
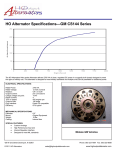
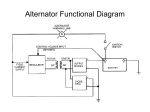
Senior Project –ECE – 2008 Power Conversion Control for a Micro-Wind Turbine Kevin Donovan, Malysa Cheng Advisors: Prof. Spinelli, Wilk Abstract With increasing demand for alternative energies, wind power is emerging as one of the earth’s viable renewable resources. Though horizontal-axis turbine designs currently dominate the market, vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs) can provide better performance in lower-class winds. Given the low average wind speeds at Union College, we have designed a hybrid VAWT with a microcontroller-based power conversion system to effectively charge a battery over a broad range of wind speeds. Goals •Safely charge a deep cycle battery •Maximize system efficiency •Broaden range of useful wind speeds •Record wind speed vs. turbine RPM data System Overview Alternator Rectifier DC-DC Converter Hybrid VAWT Design in SolidWorks Battery Inverter Load Control Algorithm Measure Wind Speed Measure Shaft RPMs Measure Battery Voltage Calculate Alternator Voltage Alternator Voltage vs. RPMs Wind Torque AC DC Storage AC Outlet 9v> Valt > 15v Log Data Determine Battery Charge State 25 Voltage (V) 20 Design Set Duty Cycle Ratio 15 10 5 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 RPMs •Alternator with rewound stator for higher voltages at lower rotational speeds •Buck/boost converter topology allows for output voltages above and below input •AGM battery for safety and depth of discharge •Anemometer and Hall-effect transistor for wind speed and RPM sensing •Basic Stamp 2psx controls DC-DC converter duty cycle and records sensor data •Parallax PWMPAL coprocessor allows Basic Stamp to output PWM signal while also running the control algorithm Buck/Boost Converter Topology Future Work Once the turbine manufacturing is completed, we will evaluate its performance in different wind speeds. With this data, the DC-DC converter can be optimized for the most frequent turbine RPMs. We will also investigate more efficient MOSFET driving techniques.