* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download All in a Flower - Trimble County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
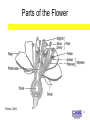
Introduction to Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources 1 Introduction to Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources All in a Flower Unit 5 – Lesson 5.2 All About Plants 2 Importance of Flowers Value to the plant – sexual reproduction Processes of reproduction: Pollination Fertilization Seeds are produced 3 Parts of the Flower Parker, 2004 4 Female Flower Parts • Ovule: The egg cell of the plant – becomes the seed when fertilized. • Pollen tube: Transfers pollen from stigma to ovule. • Pistil: Female part of flower, composed of three parts – Stigma: Collects pollen – Style: Supports stigma – Ovary: Contains one or more ovules 5 Male Flower Parts • Anther: Develops and contains pollen. • Stamen: Male part of flower, consists of two parts – Filament: Supports anther to assist with pollination – Pollen: Male sex cell 6 Supporting Parts • Petal: Protects pistil and stamens, and attracts insects for pollination. • Sepal: Outermost leaves protecting the flower during the bud stage. 7 Types of Flowers • Complete: Contains all major flower parts including petals, sepals and both reproductive organs. • Perfect: Includes both female and male reproductive parts. • Incomplete: Missing one or more of the sepals, petals, stamens, or pistils. • Imperfect: – Pistillate – lacks stamens – Staminate – lacks pistils 8 References Herren, R. V., & Donahue, R. L. (2000). Delmar’s agriscience dictionary with searchable CD-ROM. Albany, NY: Delmar. Parker, R. (2010). Plant and soil science: Fundamentals and applications. Clifton Park, NY: Delmar. Schooley, J. (1997). Introduction to botany. Albany, NY: Delmar Publishers. 9