* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Type of Cell Diversity
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
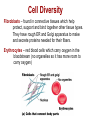
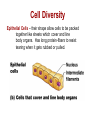
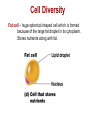
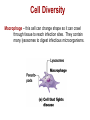
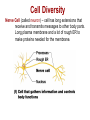
Cell Diversity Fibroblasts – found in connective tissues which help protect, support and bind together other tissue types. They have rough ER and Golgi apparatus to make and secrete proteins needed for their fibers. Erythrocytes – red blood cells which carry oxygen in the bloodstream (no organelles so it has more room to carry oxygen) Cell Diversity Epithelial Cells – their shape allow cells to be packed together like sheets which cover and line body organs. Has long protein-fibers to resist tearing when it gets rubbed or pulled. Cell Diversity Skeletal Muscle – elongated shape which allow cells to shorten (contract) moving our skeleton. They contain long protein fibers. Smooth Muscle – elongated shape too which allow our internal organs to change size Cell Diversity Fat cell – huge spherical shaped cell which is formed because of the large fat droplet in its cytoplasm. Stores nutrients along with fat. Cell Diversity Macrophage – this cell can change shape so it can crawl through tissue to reach infection sites. They contain many lysosomes to digest infectious microorganisms. Cell Diversity Nerve Cell (called neuron) – cell has long extensions that receive and transmits messages to other body parts. Long plasma membrane and a lot of rough ER to make proteins needed for the membrane. Cell Diversity Oocyte (female) – the largest cell in the body. This cell has twice as many organelles so it can distribute to new cells through growth/division. Sperm (male) – This cell is long and built for swimming. Flagellum acts as a whip to move sperm forward.