* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.3 Stars
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
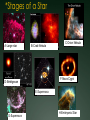
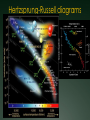
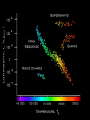
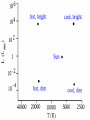
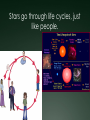
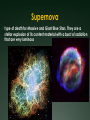
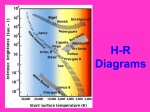
Warm Up What causes day and night? Why do we experience season’s? What divides the Earth into northern and southern hemispheres? What is a revolution? If the northern hemisphere is experiencing spring, what is the southern hemisphere experiencing? Explain the difference between nutation and precession. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Activating stratgegy 1) How many Earths do you think would fit inside the Sun? 2) How hot do you think the Sun is? 3) How much longer do you think the Sun will last? 4) How many stars do you think there are in our Milky Way? 5) How many stars do you think there are in the whole universe? Quote of the Day Life is not about waiting for the storm to subside. It’s about learning to dance in the rain! Objective & LEQ Objective: SWBAT analyze the life cycle of stars and apply it to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. LEQ: What determines the life cycle of a star and how is it applied to the HertzsprungRussell diagram? Table of Contents Left Side Item Page Right Side Items Page T-Chart Planets 0 Solar System Formation CN 1 Kepler 22b Article 0 Planetary Motion CN 3 Universe Venn Diagram 0 Star CN 5 Season’s Foldable 2 Season’s Graphic Organizer 2 HR Diagram 4 Star Foldable 4 Science GEMS of Wisdom Page Avid Strategy 0 T-Chart Planets 0 Kepler 22b Article 0 Universe Venn Diagram 2 Season’s Foldable 2 Season’s Graphic Organizer 4 HR Diagram 4 Star Foldable W I C O R Warm Up ANSWERS 1. 1 million (1,000,000!) Earths! 2. 10,000°million F! 3. About 7 billion more years 4. 200-400 billion 5. 100,000,000,000,000,000,000,000! Quiz! You may use your notes ABSOLUTELY NO TALKING First time, verbal warning and -5 points Second time, zero on your quiz Once you are finished, hold up your quiz and I will collect it. You have 3 things to finish: Make sure you have a SUMMARY written for your notes yesterday (**remember, the summary answers the LEQ)! Finish chunking/coloring notes Finish the worksheet and foldable (it was HW) *Stages of a Star A-Large star B-Crab Nebula C-Orion Nebula F-Nova Cygni D-Betelgeuse E-Supernova G-Supernova H-Embryonic Star Black Hole Video Clip http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h1iJXOUMJ pg Scientist Neil Degrasse Tyson *What are the different ways that death would result from a black hole? Characteristics of Stars Apparent magnitude: (a stars brightness as it appears from EARTH) 1. how big it is 2. how hot it is 3. how far away it is Absolute magnitude: how bright a star actually is. (ex: 2 stars with equal absolute magnitudes may have difference apparent magnitudes because one is farther away!) Luminosity measures absolute magnitude. Surface temperature: how hot a star is (measured in Kelvins) Characteristics of Stars HR Diagram: A graph that shows the relationship between the absolute magnitude and temperature of stars. The hottest main sequence stars are the brightest The coolest main sequence stars are the dimmest. Use the information on luminosity and apparent magnitude to make a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (pg. 704)! Draw your own HR Diagram using the chart on page 704 as an example!! You have 20 minutes…work smart! Hertzsprung-Russell diagrams Stars go through life cycles, just like people. What determines the life cycle of a star? Depending on how big a star is, it will follow a certain life path. FAST FACT In a few billion years, the sun’s core will run out of hydrogen fuel, triggering nuclear fusion in the surrounding shell. As a result, the sun’s outer envelope will expand, producing a red giant hundreds of times larger and brighter. Intense solar radiation will boil Earth’s oceans, and solar winds will drive away Earth’s atmosphere. Directions Complete the star foldable and lifecycle diagram using pages 707-711 in your textbook for: A) low-mass stars B) medium-mass stars (sun-like) C) massive stars *Draw the life cycle stages for the 3 types of stars This will be glued/taped onto page 6 of your notebook! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YU6X3SPZ AJo Star Nursery (nebula) The birthplace of a star where gas and dust begin to combine to form the star Protostar the beginning stages of star formation when gravity pulls in the gas and dusts from the star nursery and it begins to shine! Main Sequence Star 90% of all stars in the universe; when stars radiate (shine) energy into space Red Giants a large bright star with a cool surface. It is formed during the later stages of the evolution of a star like the Sun, as it runs out of hydrogen fuel at its center White Dwarf Thought to be the final evolutionary state of all stars whose mass is not too high—over 97% of the stars in our Galaxy; when its nuclear energy is gone, I begin to contract and appear very bright Black Dwarf Over a very long time, a white dwarf will cool to temperatures at which it is no longer visible and become a cold black dwarf; become a lump of coal in the sky when all its nuclear energy is gone Supernova type of death for Massive and Giant Blue Stars. They are a stellar explosion of its content material with a burst of radiation that are very luminous Blackhole a region of space in which the gravitational field is so powerful that nothing, including light, can escape its pull. The black hole has a one-way surface, called an event horizon, into which objects can fall, but out of which nothing can come (form of death for massive stars) Neutron star also known as a Pulsar star because of its ‘pulsating’ effect that can be seen when viewed at a specific angle. The Pulsar Star is a result of the gravitational collapse of a Giant Blue Star Stellar Match! Cut out the star stages and definitions Match the start stage with the correct definition Glue it into your notebook on page 6 Using pages 704-714, match the type of star with its description. You have 10 minutes to complete this activity. Star Story: Write a short story following a star from birth to death. Beginning At least 3 descriptive sentences about each stage. End OR Illustrate a comic book following a star from birth to death. Must have drawings AND text (speech/thought bubbles). Beginning At least 3 panels for each life stage. End Textbook Activities Read pages 703 – 704 and 706. Answer questions 4 – 5 on page 706. Read pages 707 – 714. Answer questions 1-4 on page 714. Read pages 622 – 624: Answer questions 1 and 2 on page 629. Read pages 644 – 647: Answer questions 1-6 on page 648. Exit Ticket 1. What is the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude? 2. What two characteristics of stars does a H-R diagram show? 3. Draw out the 7 consecutive stages of a sun-like star (medium-mass). 4. What type of star ends as a neutron star or black hole?