* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
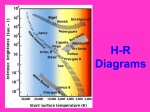
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science Star Facts Types of Stars and How They Form • Low Mass Stars • Medium Mass Stars • High Mass Stars Low Mass Stars • • • • Nebula Protostar Main Sequence Star White Dwarf • Small, cool stars • Use hydrogen slowly • Live more than 30 billion of year Medium Mass Stars • • • • • • Nebula Protostar Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf • Medium size and temperature • Live about 10 billion years High Mass Stars • • • • • • Nebula Photostar Main Sequence Star Supergiant Supernova Neutron Star or Black Hole • Hottest, most massive stars • Shortest lives: millions of years • Uses hydrogen quickly Black Holes • Formed when a supernova explodes causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. Stars Colors and Temperatures Blue Hottest Yellow Medium temperature Sun Red Coolest Starlight Brightness • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be from earth when viewed with the unaided eye. Distance can cause a dimmer star to appear to be brighter than a brighter star that is farther away. • Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light (brightness) a star actually has. This is an actual measurement. Electromagnetic Radiation • Energy that travels through space in waves • Stars give off electromagnetic radiation in different forms • Each form has its own wavelength • • • • • • Radio Waves Infrared Rays Visible Light Ultraviolet Light X-Rays Gamma Rays