* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
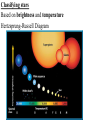
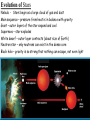
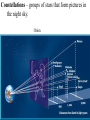
Stars, Galaxies, and Constellations Stars = objects in space, made of gases, which produce their own light and heat. Earth’s nearest star is the sun (149,600,000 km away) The next nearest star is Proxima Centauri (4.24 light years away) Light year = the distance light travels in 1 year • Light travels at 300,000 km/s, or about 9.5 trillion km in one year. Measurement in Space Parallax - the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions Nuclear Fusion = reactions occur when hydrogen atoms combine to form helium atoms. *this produces great amounts of light and heat* Different stars produce different amounts of energy. The amount of energy produced by a star determines the star’s color and surface temperature. Stars differ in composition, age, and size. *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium Classifying stars Based on brightness and temperature Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Evolution of Stars Nebula - Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust Main sequence – pressure from heat is in balance with gravity Giant – outer layers of the star expand and cool Supernova – star explodes White dwarf – outer layer contracts (about size of Earth) Neutron star – only neutrons can exist in the dense core Black hole – gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light Apparent magnitude – how bright the star appears from Earth. Absolute magnitude – how bright the star really is (if all stars were the same distance from Earth) Galaxy = system of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. Three major classes of galaxies: 1. Spiral Galaxy (Milky Way Galaxy) -disk-shaped with arms 2. Elliptical Galaxy -shaped like a football 3. Irregular Galaxy -no distinct shape Constellations – groups of stars that form pictures in the night sky. Orion Astronomers recognize 88 constellations. View of the north sky