* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ☺ PLAN 1. Ampere’s law 2. Applications
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
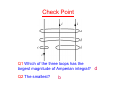
PLAN 1. Ampere’s law 2. Applications Require a high symmetry. ♣ Magnetic field due to i in a long straight wire — again. (Faster. No need to assume that the wire diameter is zero.) ♣ Magnetic field inside the wire. ♣ Solenoid. ♣ Toroid. ☺ 3. Magnetic field of a single coil. (Only along the symmetry axis. But you need to use the Biot-Savart law.) Electricity vs Magnetism Electricity Coulomb’s law Ù Gauss’ law Magnetism Biot-Savart law Ù Ampere’s law r r r Plus: FB = qv × B Ampere’s Law • Take arbitrary path around set of currents – Let ienc be total enclosed current (+ up, − down) – Let B be magnetic field, and ds be differential length along path (couterclockwise according to the right hand rule) Not included in ienc • Only currents inside path contribute! – 5 currents inside path (included) – 1 outside path (not included) r ds θ r B Check Point Q1 Which of the three loops has the largest magnitude of Amperian integral? d Q2 The smallest? b Example 2: Inside the Wire • Find B vs r inside long wire, assuming uniform current R r Example 3: Solenoid Loosely wound and short Tightly wound and long (~infinitely long)