* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 Section 2
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
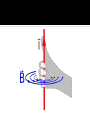
And Electricity! Chapter 8 Section 2 1820: Hans Ørsted happened to have compass close to a wire with current flowing The compass needle deflected away from magnetic north when the current was turned on and returned when the current was turned off Hypothesis: magnetic field radiates in all directions from a wire carrying an electric current Based on Ørsted’s work we know electricity and magnetism are related Any moving charge produces a magnetic field Direction of magnetic field around wire depends on direction of current If we loop a wire around a metal center, we amplify the magnetic field created by the current Electromagnet is a temporary magnet created in this way If we reverse the current, the poles of the electromagnet are reversed Electromagnets can be turned on or off by turning the current on or off Electromagnets are used in many devices: Speaker: ▪ Has a permanent magnet attached to a cone ▪ Has an electromagnet ▪ When electromagnet changes poles, it is attracted or repelled by the permanent magnet ▪ Movement of the cone makes sound ▪ HowStuffWorks "How Speakers Work" Galvanometer Galvanometer has a fixed magnet and a coil of wire making an electromagnet When current goes through electromagnet it is attracted or repelled by fixed magnet so it moves Needle attached to moving coil measures amount of current ▪ Voltmeter ▪ Ammeter Electric motor Electromagnet that can rotate between poles of permanent magnet Current through electromagnet makes it attracted and repelled to poles of permanent magnet HowStuffWorks "How does a brushless electric motor work?“ YouTube - Direct Current Electric Motor Read pages 233-239 Answer questions 1-6 on page 239: due 12/2/09