* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download is here - Electrical and Information Technology
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Signal Corps (United States Army) wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
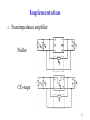
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
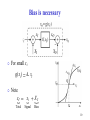
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
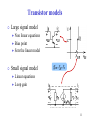
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
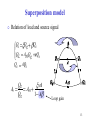
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
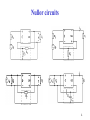
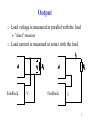
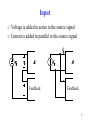
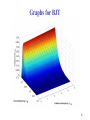
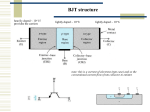
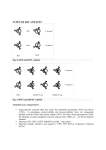
Analog Electronics Crash course part 1 Bertil Larsson Electro- and Information Technology Layout Feedback using the nullor (e.g. ideal amplifier) Transistor (bipolar and FET) Liniarization of the transistor (small signal model) Implementation (one, two or three amplifying stages) Asymptotic gain model 2 Fundamentals Why use feedback? Why do we want negative feedback? 3 Nullor circuits 4 Output Load voltage is measured in parallel with the load ”shunt”-measure Load current is measured in series with the load Feedback V Feedback I 5 Input Voltage is added in series to the source signal Current is added in parallel to the source signal Feedback Feedback 6 Amplifying elements BJT FET Both have a non linear relation between input and output signal 7 Graphs for BJT 8 Implementation Transimpedance amplifier Nullor CE-stage 9 Bias is necessary For small xi g( xi ) Note xI Total A xi xi XI Signal Bias 10 Transistor models Large signal model Non linear equations Bias point Sets the linear model Small signal model Q g m , r , ro Linear equations Loop gain 11 2 minuter Suppose you know IC for a BJT What is gm? What is r ? 12 Superposition model Relation of load and source signal Qi Qg QL At 0Qg Qc At Qc Qc AQi QL Qg At 0 A 1 A Loop gain 13 How to calculate At At 1 A 1 A 1 A At 0 1 A A At 1 A 1 At 0 1 A Discrepancy factor Neglect At∞ is set by the nullor circuit At A At 1 A 14 Calculate loopgain A Identify the ”natural” A and Feedback v1 ic2 v s 0 Controlled sources gain A ic2 v1 15 Amplifying stages CE-steg AS-steg CC-steg CB-steg Series-stage Shunt-stage negative transfer neg./pos. transfer positive transfer positive transfer negative transfer negative transfer no feedback no feedback feedback feedback feedback feedback 16 2 minuter Identify amplifying stages for the current amplifier and name them Check for negative feedback 17 Antiseries stage Small-signal model for the AS-stage is very similar to the hybrid- -model for CE-stage No connection between in- and output Parameters of the model Transconductance gm´ Input impedance r ´ Output impedance ro´ In this cource we neglect ro´ if nothing else is stated! 18 Time to get going You are to design a 2-stage V I amplifier Which stages do you choose? Motivate! Theoretical, what is the maximum loop gain? Assume you have BJT transistors at hand Which bias current influence A ? 19