* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECE311 Lab 3 Setup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
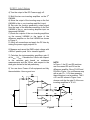
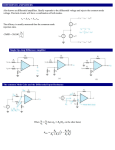
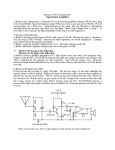
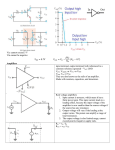
ECE311 Lab 3 Setup 1) Setup the DC power supply for +/- 15V tracking. Use the DMM to verify the rail voltages then switch off the output voltage. 2 LM3481 1 3 14 2 13 3 4 5 LM348N 1 6 LM3482 7 LM3483 8 LM3484 14 5 12 11 9 10 6 9 7 8 10 13 12 2) Select resistors found in the preliminary and measure/record their resistance. Additionally, select 2 additional equal resistors for the inverting amplifier (RA,B) shown in Figure 1. The inverting amplifier is used to generate a difference signal by inverting a 500mV, 1kHz sinusoidal signal taken from the function generator. NOTE: You want R1 = R2, R3 = R4, and RA = RB (As close as possible). The 2 x R1 and R2 values shown in Figure 2 on Page 2 are selected such that the gain of the noninverting amplifiers are as close to 10 as possible. Select, measure, and record all resistance values prior to building in this step. Next, calculate and record the expected gains for the difference and instrumentation amplifiers from the measured resistance values. Calculate the %Error using the ideal expected gain as the basis (i.e. the expected gain of the difference amp is 1 while the calculated gain based on resistance values is X). 3) Build the circuit as shown in Figure 1 on this page. Apply a 500mV sinusoid at 1kHz to the circuit from the function generator. Measure the RMS input voltage to the difference amplifier at vi1 and vi2 and the RMS output voltage from the difference amplifier using the DMM. Calculate the amplifiers gain G and the %Error with respect to the ideal expected value and the resistance calculated values. G = vo / (vi2 – vi1) vi1 is inverted by 180º. Use 2 LM348s to build. Setup the Inverting amp and the difference amp on the first LM348N. RB R2 RA R1 LM3483 vi1 R3 vsig LM3484 vi2 R4 Figure1 HINT: Labeling nodes with package pin numbers on the schematic assists in troubleshooting! + vo - ECE311 Lab 3 Setup 4) Turn the output of the DC Power supply off. 5) Build the two non-inverting amplifiers on the 2nd LM348N. A) Move the output of the inverting amp on the first LM348N to the vi1 non-inverting amplifier’s input. B) Re-route the function generator’s output signal from the input of the difference amplifier on the first LM348N to the vi2 non-inverting amplifier input on the second LM348N. C) Route the outputs of the non-inverting amplifiers on the second LM348N to the inputs of the difference amplifier on the first LM348N as shown in Figure 2. D) Verify all connections and apply the DC bias by turning the power supply outputs on. 6) Measure and record the RMS output voltage with a 500mV peak-to-peak 1kHz. sinusoid applied. 7) Calculate the instrumentation amplifiers gain G as VoRMS / ViRMS. Calculate the %Error with respect to the calculate gain based on resistance measurements and the %Error with respect to the ideal gain derived in the lab preliminary. 8) You are done. Power off all equipment and tidy the workstation. Have a good one. RB RA LM3483 NOTE: In Figure 1, the R1 and R2 resistors are now named R3 and R4 on the difference amplifier. Since R1=R3 and R2=R4 in Figure 1 for a difference amp with a gain G = 1 V/V then renaming these resistors is not a problem. The 2 x R1 and R2 values in Figure 2 are chosen such the the gain G of the noninverting amplifiers is 10 V/V. LM3481 R4 R3 2 x R1 R2 vi1 R2 R3 vsig vi2 R4 LM3482 LM3484 + vo - Figure2