* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Exam 2 Chapter 12
Survey
Document related concepts
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
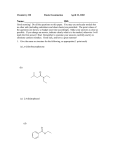
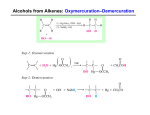
Study Guide for Exam 2 Chapter 12 From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of alkenes and alkynes. This includes cycloalkenes and compounds with more than one double bond. Where geometry is shown, identify cis and trans isomers From their names, draw condensed structural or line-angle formulas of alkenes and alkynes, including types of compounds listed in the preceding item. Know which alkenes exist as cis and trans isomers Know the four addition reactions associated with alkenes: hydrohalogenation, hydration, halogenation, and hydrogenation. For these reactions, know which ones are regioselective, and which ones require a catalyst. Be able to state Markovnikov’s rule, which of the addition reactions it applies to, and how the stability of carbocations (3o, 2o, 1o) helps to explain it. Chapter 13 From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of aromatic compounds, including those with more than one substituent on the benzene ring, and those in which the benzene ring is regarded as a substituent (phenyl ) group. From their names, draw structural formulas of aromatic compounds including types of compounds listed in the preceding item. Know the names and structures for the following benzene derivitives: toluene, phenol, aniline, anisole, benzoic acid, and benzaldehyde. Be able to complete chemical equations for characteristic substitution reactions of benzene and its derivitives (halogenations, sulfonation, and nitration), writing structures for reactants and/or products when appropriate. Also, be able to predict if a reaction would happen or not, given the reagents and/or catalysts for the reaction. Know that phenols are anti-oxidants and that phenol is a weak acid, and thus, can neutralize a base. Chapter 14 From their structural or line-angle formulas, write IUPAC and common names of alcohols and thiols, and common names for ethers. From their names, draw condensed structural or line-angle formulas of alcohols, thiols, and ethers Describe the physical properties of alcohols, thiols, and ethers. Know the attractive forces between these molecules, their relative strengths, and their effects on solubility in water and melting and boiling points. Be able to complete chemical equations for characteristic reactions of alcohols (acid-base, dehydration, and oxidation) writing structures for reactants and/or products when appropriate. Also, be able to predict if a reaction would happen or not, given the reagents and/or catalysts for the reaction. For oxidation reactions of alcohols, know when ketones, aldehydes, or carboxylic acids are formed Know the oxidation / reduction reaction of a thiol (formation of disulfide bonds).