* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 2 Card Sort
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
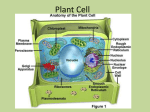
Definition of homeostasis Maintaining a constant internal environment How do you find the total magnification when using a compound microscope? Definition of cell specialization Cells express small sections of the DNA allowing many types of cells to be created Which part of the microscope controls the amount of light hitting the specimen? Purpose of compound light microscope Observe small, living, organisms in order to study cell process and behaviors Where is the diaphragm on a compound microscope? What did Robert Hooke do? Look at cork under a microscope and name the units cells What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek do? Looked at pond water and saw cells What did Matthias Schleiden do? Concluded all plants are made of cells Define prokaryotic What is an example of a prokaryotic cell? Define eukaryotic Multiply the magnification of the eyepiece and objective Function of the ribosome Puts amino acids together to synthesize (make) proteins Diaphragm Function of the mitochondria Break sugars down to create usable energy molecules for the cell Under the stage Identify the cell structure that exist only in plant cells chloroplasts A small, simple cell that does not have a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles Which cell structure is the location of protein production because ribosomes are attached to it Rough endoplasmic reticulum Bacteria Which cell structure packages the proteins after they are made Golgi apparatus aka golgi body Larger, more complicated cells that have a nucleus and other complex organelles What happens to protein after they are packaged? Some leave the cell, others are used to build cell structures What did Theodor Schwann do? What did Rudolf Virchow do? Definition of an organ system What is the cell wall made of? What are the two general categories of eukaryotic cells? Plant and animal cells What is the function of the cell wall? Protect the cell and give the cell a particular shape Purpose of cell specialization Each cell can perform different tasks allowing the organism to be larger and more complex What is the function of the cell membrane? Controls what enters and leaves the cell A group of organs working together Function of the nucleus Contains the DNA which provides the cells with all instructions and controls its activities Which cell structures are found in every cell? Cell membrane and ribosomes Strong fibers that form a structure in order to protect the cell Which macromolecule imbedded in the cell membrane helps to move thing in and out of the cell proteins What are hormones? Proteins that are used to communicate with other cells and trigger cell activities Define diffusion The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration What types of cell transport occur without energy being used? Osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion Concluded all animals are made of cells All cells come from existing cells What organelles exist only in animal cells? Centrioles What causes diffusion The random movement of particles as they bump into each other and bounce off in opposite directions Define dynamic equilibrium There is an equal concentration on either side of a membrane so particles move but at the same rate so it doesn’t change What types of cell transport require energy? Active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis Why do blood cells burst when placed in pure water? Water rushes into the cell where there is a lower concentration of water What would happen to a cell if it was placed in very salty water? It shrinks Define osmosis Draw the mitochondria Draw the plasma membrane Draw the cell wall Draw the nucleus Draw the nucleolus Draw the rough endoplasmic reticulum Draw the smooth endoplasmic reticulum Draw a chloroplast Draw a vacuole of a plant cell Draw the golgi apparatus Draw the smooth endoplasmic reticulum Draw the cytoplasm Draw centrioles The movement of water from the side of the membrane with more to the side with less Characteristics of living things Evolve over the course of several generation An individual can adopt to better survive Have DNA (genetic code) Reproduce Move Grow and develop Respond to environment Made of cells Metabolize (break down and build structures) Order of the levels of organization Atom Molecule Organelles Cell Tissue Organ Organ system Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biome Biosphere The three points to the cell theory All cells are created by existing cells All living things are made of cells Cells are the smallest function units of living things What are some examples of maintaining homeostasis in humans? Insulin being released to regulate blood sugar concentrations Maintaining a constant temperature of 98.6 Maintaining a constant pH in all body solution such as the stomach fluid and blood