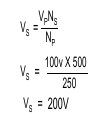* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformers - Hingham Schools
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
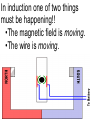
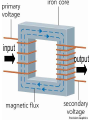
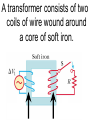
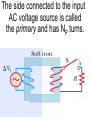
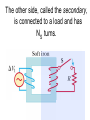
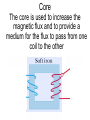
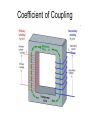
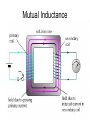
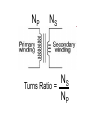
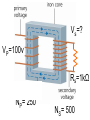
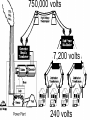
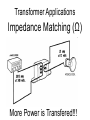
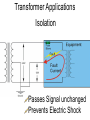
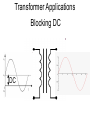
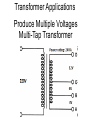
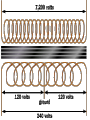
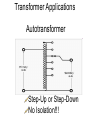
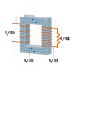
Transformers Test Friday 3/30/12 Electromagnetic Induction Induction is the process of producing (inducing) a voltage by passing a wire through a magnetic field. Generator In induction one of two things must be happening!! •The magnetic field is moving. •The wire is moving. input output A transformer works with AC voltages, since the magnetic field must be changing to induce a voltage in the coils. Transformer Designing a Transformer Frequency Voltage Power Transformer Rating Transformer are rated in Volt-Amperes (VA) Volt Amperes are used to determine the Maximum Current the transformer can handle. A transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around a core of soft iron. The side connected to the input AC voltage source is called the primary and has NP turns. NP NS The other side, called the secondary, is connected to a load and has NS turns. NS Core The core is used to increase the magnetic flux and to provide a medium for the flux to pass from one coil to the other Coefficient of Coupling The measure of how good the transformer is. Scale of 0 to 1 1 – All the magnetic Flux lines cut the Secondary Winding 0 – None of the magnetic Flux lines cut the Secondary Winding Coefficient of Coupling Mutual Inductance Mutual Inductance The fact that a change in the current of one coil affects the current and voltage in the second coil is quantified in the property called mutual inductance. Turns Ratio The turns ratio of a transformer is the ratio of number of windings of primary side to the secondary side of the transformer. NP NS NP NS NS Turns Ratio = NP Voltage Relationships The voltages are related by: NP V P = NS V S Voltage Relationships When NS > NP, the transformer is referred to as a step-up transformer. Voltage Increases Voltage Relationships When NS < NP, the transformer is referred to as a step-down transformer. Voltage Decreases Power The power input into the primary equals, at best, the power output at the secondary. Power In = Power Out IPVP = ISVS Power IPVP = ISVS (This assumes an ideal transformer.) If VS increases, as in a step up transformer, IS must decrease. If VS decreases, as in a step down transformer, IS must increase. Power Efficiency •You don’t get something for nothing!!!! •In real transformers, power efficiencies typically range from 90% to 99% (0.9 to 0.99) Vs=? VP=100v Rs=1kΩ NP= 250 NS= 500 V P NS VS = NP VS 100v X 500 = 250 VS = 200V Power Grid 750,000 volts 7,200 volts 240 volts Transformer Applications Impedance Matching (Ω) More Power is Transfered!!! Transformer Applications Phase Shifting Transformer Applications Isolation Passes Signal unchanged Prevents Electric Shock Transformer Applications Blocking DC DC Transformer Applications Produce Multiple Voltages Multi-Tap Transformer Transformer Applications Autotransformer Step-Up or Step-Down No Isolation!!! VP=100v Rs=1kΩ NP= 250 NS= 500 Ch 12: AC Pages 122 – 128 Answer Question through Chapter Write down Questions and Answers AC Worksheets: 2-1 Lab 1: Book 2 “DC and AC” Problem Worksheets 4 Simulations – Computer Lab Due 3/26th Test 3/26th Ch 18: Transformers Pages 168 – 174 Answer Question through Chapter Write down Questions and Answers Transformer Worksheets: Lab 2-14 Lab: 29 Old Book Problem Worksheets Video Worksheet – “Generating Electricity” Due 3/26th Test 3/26th