* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
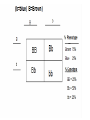
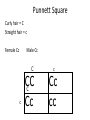
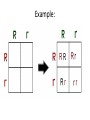
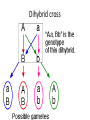
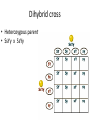
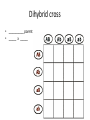
Homozygous/ Purebred - TT, BB Heterozygous/ Hybrid – Tt, Bb Punnett Square • Punnett square is a chart which shows/predicts all possible gene combinations. It shows all of the possible combinations of male and female gametes Punnett Square • the dominant gene for black fur "F,' and the recessive gene for yellow fur "f.“ • "Heterozygous" means it has two different alleles (Ff). • "Homozygous dominant" means it has two copies of the dominant allele (FF). • "Homozygous recessive" means two copies of the recessive allele (ff). Any parent that shows the recessive trait (has yellow fur) belongs to this category. • the female bear is heterozygous for fur color (Ff). We can conclude that: • we have two boxes with Ff (heterozygous). 25% + 25% = 50%, so each child has a 50% chance of inheriting Ff genes. • The other two boxes are each ff (homozygous recessive). Each child has a 50% chance of inheriting ff genes. • there are two squares with at least one F, so each child has a 50% chance to have black fur. There are two squares with ff, so each child has a 50% chance to have yellow fur. Draw the punnett square: • Mother (heterozygous) Bb • Father (heterozygous) Bb • Dominant gene for brown eyes (B), recessive gene for blue eyes Example: Brown and blue eyes • What can you conclude from the possibilities. Draw the Punnett Square: Curly hair = C Straight hair = c Female Cc Male Cc Punnett Square Curly hair = C Straight hair = c Female Cc Male Cc C c CC C Cc c Cc cc Example: Example: • TT = 5 times • Tt = 13 times • tt = 2 times 90% offspring are tall and 10% offspring short 5 x5 : 13 x 5: 2 x 5 • TT : Tt : tt = 25% : 65% : 10% Probability and Punnett square Monohybrid • Genetics is the study of heredity and variation in organisms. • A hybrid is the offspring produced when two genetically different parents are crossed. This usually results in a heterozygous individual. • Monohybrid cross: In a monohybrid cross, organisms differing in only one trait are crossed. Dihybrid cross • A dihybrid cross involves a study of inheritance patterns for organisms differing in two traits. • A dihybrid cross is a cross between two individuals that are both heterozygous for two different genes. RrYy x RrYy Dihybrid cross • Heterozygous parent • RrYy x RrYy • RY, Ry, rY, ry (parent 1) and RY, Ry, rY, ry (parent 2) 4x4 Punnet square Dihybrid cross • Heterozygous parent • RrTt x RrTt Dihybrid cross Dihybrid cross • Heterozygous parent • SsYy x SsYy Dihybrid cross • __________ parent • _____ x _____