* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 15-3 - Brookings School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
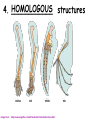
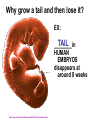
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Darwin Presents his Case Chapter 15-3 Image from: Biology by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing©2006 http://groups.wfu.edu/ModelUN/images/Cover/Oranges.jpg http://www.fx.clemson.edu/~ablank/126436919.Broccoli.jpg http://www.butterball.com/en/images/plan_n_prep/preparing/carving1.jpg THINK ABOUT IT What do oranges, broccoli and Butterball turkeys have to do with EVOLUTION? (Answers to come in this slide show!) After Darwin returned to England in 1836 he filled notebooks with his ideas, but he did not publish his ideas disagreed with the because they ________ fundamental scientific beliefs of his day. He asked his wife to publish his ideas when he died ______. http://www.elsie.brandeis.edu/images/journals.gif In 1858 another naturalist, Alfred Russel Wallace wrote an _________________, Malaysia that essay describing his work in _______ summarized the same ideas Darwin _____ had been thinking about for 25 years! http://www.thesecondevolution.com/wallace&darwin.jpg Suddenly Darwin had incentive to publish the results of his work! In 1859 On the Origin of Species ____________________ evidence presented _______ for Darwin’s ideas about how living things change called NATURAL SELECTION __________________ http://www.loc.gov/exhibits/world/images/s125.jpg http://sixthsense.osfc.ac.uk/chemistry/atomic_structure2/atom.gif Isn’t evolution just a theory? THEORY A __________is a well supported testable explanation of happenings in the NATURAL _________ world Ex: gravitational theory atomic theory cell theory http://www.avgoe.de/StarChild/DOCS/STARCH00/questions/apple_falling.gif WHAT IS DARWIN’S THEORY? VARIATION is found GENETIC___________ naturally in all populations http://www3.nationalgeographic.com/animals/images/primary/zebra-herd.jpg WHAT IS DARWIN’S THEORY? ______________________ STRUGGLE FOR EXISTANCE means that members of each species must COMPETE ________ for food, space, and other RESOURCES __________. http://www.wasatchcomputers.net/gallery/elk_fight.jpg WHAT IS DARWIN’S THEORY? Some organisms in a ________ population less likely to survive. are ________ http://www.cartoonstock.com/newscartoons/cartoonists/rrs/lowres/rrsn69l.jpg WHAT IS DARWIN’S THEORY? SURVIVAL OF THE FITTEST _____________________ organisms which are better adapted survive and to the environment will ______ reproduce passing on their _____. genes ________, http://www.poster.net/bedard/bed202.jpg VOCAB http://www.cartoonstock.com/newscartoons/cartoonists/cga/lowres/cgan170l.jpg Ability of an individual to survive ______ and reproduce in its specific ____________ environment = fitness ______ VOCAB inherited characteristic that Any ___________________ of survival increases an organism’s chance ______________ ADAPTATION = _____________ http://www.wildlife-traps.com/skunks.html http://www.atomtigerzoo.com/photos/images/20060421233733_duckfeet.jpg http://www.3kitty.org/travelrama/Photos/123-21-4x6.jpg WHAT IS DARWIN’S THEORY? Over time, natural selection CHANGES in the results in ________ inherited characteristics of a POPULATION __________. increase a These changes ______ species’ fitness _____ in its environment. How Does Evolution Really Work? WHAT IS DARWIN’S THEORY? DESCENT WITH MODIFICATION ____________________________ each species has descended with changes from other species over time. This idea suggests that all living species are related to each other. and that all species, living and extinct, COMMON ANCESTOR share a _________________. EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION: Artificial 1. __________ selection 2. ________________ Fossil record Geographic 3. ___________distribution Homologous 4. ___________ structures 5. _______________ Embryology DNA 6. _______________ 7. see natural selection happen ARTIFICIAL SELECTION WORKS variation Nature provides the____________ mutation and through _________ _________ sexual reproduction useful Humans select traits they find ______. EX: We have selected for and bred cows to produce more milk, turkeys with more breast meat, etc. http://www.pp3moo.com/hm2cow.jpg http://lazerbrody.typepad.com/photos/uncategorized/turkey.gif Breeds of Dogs Chihuahua – bred from Techichi of Mexico by Mayans, had religious significance Saint Bernard – bred by monks around 1050 A.D. to rescue travelers of mountain passes in the Swiss Alps between Italy and Switzerland Irish Wolfhound – bred in Ireland to hunt wolves and elk Dachshund – bred in Germany as early as the 15th century to hunt badgers SLIDE FROM: BIOLOGY by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing©2006 ____________________________ ARTIFICIAL SELECTION WORKS BIOLOGY by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing©2006 http://groups.wfu.edu/ModelUN/images/Cover/Oranges.jpg http://www.fx.clemson.edu/~ablank/126436919.Broccoli.jpg http://www.butterball.com/en/images/plan_n_prep/preparing/carving1.jpg THINK ABOUT IT Now you know what broccoli and Butterball turkeys have to do with evolution! (Answers about oranges to come in this slide show!) How Do We Know Evolution Happens? 2. The Fossil Record – Fossils are the _______ remains ______ _________________ of ancient organisms found in layers of rock in the Earth. How Do We Know Evolution Happens? The layers of rock tell the history of the Earth. The fossils in the rocks LIFE tell the history of ______ The fossils are the same age as the rock they are found in. TRANSITIONAL FOSSILS HAVE BEEN FOUND Scientific American; Dec 2005; Vol 293; p100-107 If Darwin’s theory is correct you would expect to find: Closely related yet different species living in a geographic region as they spread into nearby habitats and evolve. That’s EXACTLY what we do see! http://www.newtonswindow.com/problem-solving.htm REMEMBER THE GALAPAGOS TORTOISES Intermediate vegetation Intermediate necks Little vegetation Long necks Image from: BIOLOGY by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publisher©2006 Lots of vegetation Short necks Tortoises adapted to different habitats as they spread from the mainland to the different islands. DIVERGENT =___________ evolution http://images.encarta.msn.com/xrefmedia/aencmed/targets/illus/ilt/T014608A.gif GALAPAGOS FINCHES The _____ beaks of Galapagos finches have adapted ______ to eating a variety _____ of foods _____. If Darwin’s theory is correct: you would also expect to find different species living in similar habitats becoming more alike ____________ as they adapt to where they live That’s EXACTLY what we do see! http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fish/gallery/descript/TigerShark/scars.JPG http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/shared/spl/hi/guides/456900/456973/html/nn1page1.stm Whales and sharks have a similar body design even though they are very different organisms (one is a fish; the other, a mammal) because they have both adapted to living in a similar environment. CONVERGENT evolution = ____________ Whales are closely related to wolves, but don’t look or act much like them = divergent evolution Whales are distantly related to sharks, but look and act more like them = convergent evolution 4. HOMOLOGOUS ____________ structures Image from: http://www.angelfire.com/ab7/evolution12/evolutionclues.html 4. Homologous Body Structures – Structures that look different but are made from the same bones because they are made from the same embryonic cells Image from: http://www.angelfire.com/ab7/evolution12/evolutionclues.html 4. Homologous Body Structures – Some homologous structures are vestigial and have no useful _______ function even though they are still present hipbones Ex: ________in whales and boa constrictors http://www.txtwriter.com/backgrounders/Evolution/EVpage12.html Most mammals have a pouch between their small and large intestine that contains bacteria cecum to digest plants called a _____. In humans the cecum is shrunken and unused. appendix It is our _________ http://www.medicalgeo.com/images/appendix.gif Why grow a tail and then lose it? EX: TAIL ________in HUMAN EMBRYOS disappears at around 8 weeks http://www.suite101.com/files/topics/6234/files/tail_HumanTail.gif EX: Vestigial organs Skinks are a type of lizard whose ______ legs have become so small they no longer function in walking. . Why would an organism possess organs that no longer work? http://www.medicalgeo.com/images/appendix.gif http://www.medicalgeo.com/images/appendix.gif http://www.txtwriter.com/backgrounders/Evolution/EVpage12.html One explanation: The genes to make the organ are present but have been mutated so they no longer have the information to make the part function. 5.Similarities in ____________ Embryology Vertebrate embryos look very similar. Image from: http://calspace.ucsd.edu/virtualmuseum/litu/03_3.shtml Embryonic cells develop in the same order to produce the same tissues and organs of all vertebrates, suggesting that they all evolved from a common ancestor _______________. Image from: http://io.uwinnipeg.ca/~simmons/16cm05/1116/16anim3.htm DNA 6. SIMILARITIES IN_______ Similarities in DNA and protein sequences suggest relatedness Image from: BIOLOGY AP EDITION by Campbell and Reece; Prentice Hall Publishing©2005 Human- 46 chromosomes Chimpanzee- 48 chromosomes karyotypes suggest Similar _________ relatedness Human: http://www.nationmaster.com/wikimir/images/upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/1/18/300px-Human_karyogram.png Chimpanzee: Middle School Life Science , published by Kendall/Hunt. 1. BANDING ________PATTERN MATCHES If you take the two smaller chromosomes apes have that we don’t, and place them end to end: the banding pattern is identical to the #2 human ________ chromosome we have that they don’t http://www.evolutionpages.com/chromosome_2.htm 2. TELOMERES __________ in the middle Chromosomes have special sequences called telomeres at their ends to protect the strands during replication. http://joannenova.com.au/Speaking/Morslids.html 2. TELOMERES IN MIDDLE If two chromosomes were joined, you would expect to find telomere sequences in the middle. Human chromosome #2 has telomeres at the ends AND in the middle → → → http://www.evolutionpages.com/chromosome_2.htm 3. EXTRA _____________ CENTROMERE If two chromosomes were joined, you would expect to find multiple centromeres. Human chromosome #2 has a second non-working centromere region → http://www.evolutionpages.com/chromosome_2.htm http://groups.wfu.edu/ModelUN/images/Cover/Oranges.jpg http://www.fx.clemson.edu/~ablank/126436919.Broccoli.jpg http://www.butterball.com/en/images/plan_n_prep/preparing/carving1.jpg THINK ABOUT IT What do oranges, broccoli and Butterball turkeys have to do with EVOLUTION? (Answers to come in this slide show!) Did you ever wonder why dogs and cats don’t need to eat fresh fruit, but you do? http://www.naturescornermagazine.com/NaturesBlog/images/dog%20care%20in%20summer.jpg http://www.alpo.com/where.aspx Fish, amphibians, reptiles, and most mammals can make their own VITAMIN C but humans need to eat _________, fresh fruit or they end up with ________. SCURVY http://www.med.uc.edu/departme/cellbiol/Image7.gif http://www.rachelleb.com/images/2005_02_22/scurvy.jpg Human DNA contains the gene that codes for the enzyme to make VITAMIN C but it is non-working. ____________, Guess what other group of organisms lack the ability to make their own Vitamin C? PRIMATES… ______________ including chimpanzees, orangutans, gorillas, and other apes. http://groups.wfu.edu/ModelUN/images/Cover/Oranges.jpg Humans have many other nonfunctional vestigial genes called ________________. PSEUDOGENES EX: Humans have more than 99 different odor receptor genes, but more than 70% of them are nonfunctional ___________. http://www.animationplayhouse.com/new/dogs2.html http://unraveling.typepad.com/photos/uncategorized/nose_1.jpg WHY DOES EVOLUTION MATTER NOW? Can see Natural selection happen 7.____________________________ EX: Peppered Moths There is a natural variation in populations of peppered moths. Typica Carbonaria Typica form - lighter ________________ Carbonaria form - darker ___________________ http://www.hipusa.com/eTools/webmd/A-Z_Encyclopedia/tuberculosis.jpg http://www.hhmi.org/askascientist/images/hiv.gif The ___________ light colored form was the predominant form in England _____________________________. prior to the Industrial Revolution Around the middle of the 19th century the ______ darker form began to appear. It was first reported in 1848. By 1895 98% of the moths in Manchester were the dark ____ variety. In recent years, the burning of cleaner fuels and Clean Air regulations has reduced the pollution there and the lighter ______ colored moths have increased in numbers. http://www.hipusa.com/eTools/webmd/A-Z_Encyclopedia/tuberculosis.jpg 7.____________________________ Can see Natural selection happen EX: Changes in disease-causing microbes that produce new organisms and new __________. diseases Bird flu _______ HIV ___ http://www.hhmi.org/askascientist/images/hiv.gif Antibiotic-resistant tuberculosis __________________________ http://www.hipusa.com/eTools/webmd/A-Z_Encyclopedia/tuberculosis.jpg Should the Use of Antibiotics Be Restricted? Read the Issues in Biology article on p. 403 in your text. Then watch the video Why Does Evolution Matter Now? and discuss the question: Should the use of antibiotics be restricted? PBS EVOLUTION VIDEO CLIPS Isn’t Evolution Just a Theory? QuickTime Who was Charles Darwin? QuickTime How Do we Know Evolution Happens? QuickTime How Does Evolution Really Work? QuickTime | Why Does Evolution Matter Now? QuickTime Why is Evolution Controversial Anyway? QuickTime SOUTH DAKOTA SCIENCE STANDARDS NATURE OF SCIENCE Indicator 1: Understand the nature and origin of scientific knowledge. 9-12.N.1.1. Students are able to evaluate a scientific discovery to determine and describe how societal, cultural, and personal beliefs influence scientific investigations and interpretations. (EVALUTION) • Recognize scientific knowledge is not merely a set of static facts, but is dynamic and affords the best current explanations. • Discuss how progress in science can be affected by social issues. SOUTH DAKOTA SCIENCE STANDARDS NATURE OF SCIENCE Indicator 1: Understand the nature and origin of scientific knowledge. 9-12.N.1.2. Students are able to describe the role of observation and evidence in the development and modification of hypotheses, theories, and laws. (SYNTHESIS) • Recognize and analyze alternative explanations and models. • Evaluate the scientific accuracy of information relevant to a specific issue SOUTH DAKOTA SCIENCE STANDARDS NATURE OF SCIENCE Indicator 1: Understand the nature and origin of scientific knowledge. 9-12.N.1.2. Students are able to describe the role of observation and evidence in the development and modification of hypotheses, theories, and laws. (SYNTHESIS) • Recognize and analyze alternative explanations and models. • Evaluate the scientific accuracy of information relevant to a specific issue Core High School Nature of Science Performance Descriptors High school students performing at the ADVANCED level: High school students performing at the PROFICIENT level: given a scientific discovery, evaluate how different societal, cultural, and personal beliefs influenced the investigation and its interpretation given a scientific discovery narrative, determine and describe how societal, cultural, and personal beliefs influenced the investigation and its interpretation; given a scientific discovery narrative, identify the High school cultural and personal beliefs that influenced the students performing investigation. at the BASIC level: SOUTH DAKOTA SCIENCE STANDARDS LIFE SCIENCE Indicator 2: Analyze various patterns and products of natural and induced biological change. 9-12.L.2.2. Students are able to describe how genetic recombination, mutations, and natural selection lead to adaptations, evolution, extinction, or the emergence of new species. (SYNTHESIS) Examples: behavioral adaptations, environmental pressures, allele variations, bio-diversity • Use comparative anatomy to support evolutionary relationships . • Recognize and analyze alternative explanations and models. • Evaluate the scientific accuracy of information relevant to a specific issue Core High School LIFE Science Performance Descriptors High school students performing at the ADVANCED level: High school students performing at the PROFICIENT level: High school students performing at the BASIC level: •predict the impact of genetic changes in populations (mutation, natural selection and artificial selection, adaptation/extinction); •predict how life systems respond to changes in the environment; • identify DNA as the structure that carries the genetic code; • identify that genetic traits can be transmitted from parents to offspring;