* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Midsegment Thm paragraph proof
Survey
Document related concepts
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
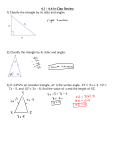
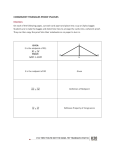
Midsegment Theorem GEOMETRY NAME_________________________ DATE __________ Per.___________ Quadrilaterals is the midpoint 1. M of TR. T a) Measure each of the following angles. D is the midpoint of TI. m ∠TMD = m ∠MDT = m ∠TRI = m ∠RIT = b) As these are corresponding angles, what can you conclude? M D c) Measure each of the following segments. MD = RI = d) Notice anything special? R I 2. MIDSEGMENT THEOREM: In any triangle, the segment joining the midpoints of any two sides -- called the -- is to the third side and the length of that side. 3. GIVEN: MD is the midsegment of ∆ISE. I M S D G PROVE: MD // SE and MD = SE÷2 E Extend MD to G so that MD ≅ DG. D is a midpoint of IE so ID ≅ ____. Therefore, D is the midpoint of both ___ and ___. Since its diagonals ________ each other, quadrilateral MIGE is a ______________. Hence, GE // IM by ___________ of a parallelogram. Since opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent, GE ≅ ___. Because M is a midpoint of ___, IM ≅ ___. Therefore, GE = MS by the _________ property. As GE // IM, ___ is also parallel to IS, and therefore, MS. With GE & MS being parallel and congruent, SEGM is a _________. Hence, MG is __________ to SE by definition of a ______________ so MD // SE since D is on MG. MD = MG÷2 by the __________ Theorem, and MG ≅ ___ as opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Finally, MD = SE÷2 by _____________.