* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HALF AND FULL WAVE RECTIFIERS
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Signal Corps (United States Army) wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
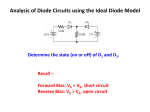
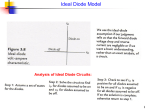
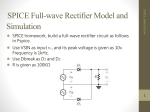
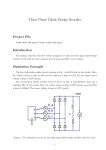
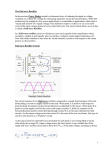
Adnan Menderes University EE210 Circuit Theory-II HALF AND FULL WAVE RECTIFIERS A device is capable of converting a sinusoidal input waveform into a unidirectional waveform with non-zero average component is called a rectifier. Half-Wave Rectifier Since diodes restrict the flow of current to one direction, they can be used to convert an AC power supply, which switches polarity from + to - many times a second, into a straight DC supply. The simplest rectifier uses one diode, like this: Called a half-wave rectifier, this circuit takes an AC signal in and chops off anything that falls below 0 Volts. (In addition, the input signal have a voltage drop of 0.2-0.3 V or 0.6-0.7 V depends on the materials of diode that is Germanium or Silicon, respectively.) Signal In: Signal Out (Half-wave): Summary of Main Characteristics: A practical half wave rectifier with a resistive load is shown above. During the positive half cycle of the input the diode conducts and all the input voltage is dropped across RL. During the negative half cycle the diode is reverse biased so the output voltage is zero. The filter is simply a capacitor connected from the rectifier output to ground. The capacitor quickly charges at the beginning of a cycle and slowly discharges through RL after the positive peak of the input voltage. The variation in the capacitor voltage due to charging and discharging is called ripple voltage. Generally, ripple is undesirable, thus the smaller the ripple, the better the filtering action. Ripple factor is an indication of the effectiveness of the filter and is defined as Ripple factor = √ where Vrms = 𝑉𝑚 2 , Vdc = 𝑉𝑚 π (𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠)2 (𝑉𝑑𝑐)2 −1 and Vm: is the maximum peak value in one half of the signal The ripple factor can be lowered by increasing the value of the filter capacitor or increasing the load capacitance. Full-Wave Rectifier The half-wave rectifier chopped off half our signal. A full-wave rectifier flips the - half of the signal up into the + range. When used in a power supply, the full-wave rectifier allows us to convert almost all the incoming AC power to DC. A full-wave rectifier uses a diode bridge, made of four diodes, like this: Here's what the circuit looks like to the signal as it alternates: Rectified output voltage/current waveforms So, if we feed our AC signal into a full wave rectifier, we'll see both halves of the wave above 0 Volts. Since the signal passes through two diodes, the voltage out will be lower by two diode drops (for example; 1.2 Volts). AC Wave In: AC Wave Out (Full-Wave Rectified): If we're interested in using the full-wave rectifier as a DC power supply, we'll add a smoothing capacitor to the output of the diode bridge. Summary of Main Characteristics: A full wave rectifier with a resistive load is shown above. During the positive and negative half cycle of the input the diode conducts and all the input voltage is dropped across RL. The filter is simply a capacitor connected from the rectifier output to ground. The capacitor quickly charges at the beginning of a cycle and slowly discharges through RL after the positive peak of the input voltage. The variation in the capacitor voltage due to charging and discharging is called ripple voltage. Generally, ripple is undesirable, thus the smaller the ripple, the better the filtering action. Ripple factor is an indication of the effectiveness of the filter and is defined as Ripple factor = √ where Vrms = 𝑉𝑚 √2 half of the signal , Vdc =2 x 𝑉𝑚 π (𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠)2 (𝑉𝑑𝑐)2 −1 and Vm: is the maximum peak value in one