* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EEG 443
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
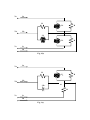
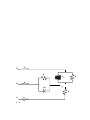
EE 340L EXPERIMENT # 1 MEASUREMENT OF POWER QUANTITIES A. SINGLE-PHASE CIRCUIT: Select R = 150Ω, L = 0.4H, C = 20μF, and V = 120V for the single-phase circuits shown. 1. Parallel R-L-C Circuit: Connect the circuit in Fig. l (a). Measure and record the source voltage VS, the source current IS, and real power supplied by the source for the following cases: a) Only R is witched ON (with L and C switched OFF) b) Only L is witched ON (with R and C switched OFF) c) Only C is witched ON (with R and L switched OFF) d) Only R and L are switched ON (with C switched OFF) e) Only R and C are switched ON (with L switched OFF) f) Only L and C are switched ON (with R switched OFF) g) All the elements (R, L, C) are switched ON. B. THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS: B1. Balanced 3Ф 4-wire Load: Connected a balanced three-phase R-L load as shown in Fig. l(b) with L = 0.4H and R = 150 Ω. 1. Measure the following: a) The phase voltages Van ,Vbn, Vcn, and the line voltages Vab ,Vbc, Vca. a) The line currents Ia, Ib, Ic, and the neutral wire In (use the smallest scale for In). b) The total real and reactive powers supplied by the three-phase source (use the three-phase meters). 2. Remove the neutral wire from the circuit and note any changes in the power flows. B2. Unbalanced 3Ф 4-wire Load: Connect the unbalanced circuit in Fig. l(c) with L = 0.4H and R = 150Ω, and C = 20μF. Measure the following: a) the phase voltage Van, line current Ia, and power supplied by phase “a”. b) the phase voltage Vbn, line current Ib, and power supplied by phase “b”. c) the phase voltage Vcn, line current Ic, and power supplied by phase “c”. d) The neutral current In. B3. Unbalanced 3Ф 3-wire Load: Now disconnect the connection between the neutral of the source and the neutral of the circuit in Fig. l (d). 1. Repeat a), b) and c) above. 2. Measure the line-to-neutral voltages VbN, VcN, and VaN (where N is the neutral point of the load rather than the source). 3. Finally measure the voltage VNn, i.e., the voltage of the neutral point of the load with respect to the neutral point of the source. QUESTIONS: Single-phase circuit: 1. Compute the apparent power S, the reactive power Q and load Power Factor (PF) from the measured voltage, current and real Power for each of the 7 cases a) through g). Indicate for each case whether the power factor is lagging or leading. 2. Use the measured value of the source voltage and the given values of R, L, and C to compute the source current and real power supplied by the source for 7 cases a) through g). Compare these calculated values with the measured values. Explain the sources of errors. 3. Calculate the capacitor value that is needed in case g) that will result in minimum source current. Three-phase balanced circuit: 1. Compare the various voltages and currents that were measured, and then determine how well the source is balanced, and how well the load is balanced? Three-phase 4-wire unbalanced circuit: 1. Calculate the phase angles of the three line currents with respect phase voltage Van. Compute the sum of these currents (as phasors) and compare the result to the measured neutral current. Discuss the sources of error. Three-phase 3-wire unbalanced: 1. Use the measured values of the phase voltages (Van , Vbn, Vcn) and the values of R, L, and C to compute the magnitude and phase angle of VNn. Compare the magnitude of this voltage with the measured value. 2. Use the result found in 1) above to compute the current, active and reactive power of each of the 3 sources. Again compare your results with the corresponding measured values. IS + VS IL jXL IR Fig. 1(a) R IC -jXC Va Ia R Vb jXL R jXL R jXL R Ib jXL Vc Ic In Fig. 1(b) Va Ia R Vb Ib -jXC N R Vc Ic In Fig. 1(c) Va Ia R jXL Vb R Ib -jXC N R Vc Ic In n Fig. 1(d)