* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Premedication mgmc
Survey
Document related concepts
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
History of general anesthesia wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
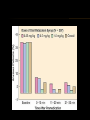
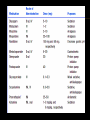
Dr. S. Parthasarathy MD., DA., DNB, MD (Acu), Dip. Diab. DCA, Dip. Software statistics PhD (physio) Mahatma Gandhi medical college and research institute – Puducherry – India PREMEDICATION WHY WE NEED ?? Sedation and anxiolysis Analgesia and amnesia Antisialagogue effect To maintain hemodynamic stability, including decrease in autonomic response To prevent and/or minimize the impact of aspiration To decrease postoperative nausea and vomiting Prophylaxis against allergic reaction VAAAAAS-- pneumonic BEFORE WE WRITE !! Patient age and weight Physical status Levels of anxiety and pain Previous history of drug use or abuse History of postoperative nausea, vomiting or motion sickness Drug allergies Elective or emergency surgery Inpatient or outpatient status Familiarity with drugs PSYCHOLOGY Anxiety 40 -80 % 55 % in one study Counselling Drugs WHEN TO ADMINISTER Drug , route Choose so that the peak action time is at their entry into the operating room BENZODIAZEPINES Sedation Anxiolysis No nausea but No analgesia Excess sedation, paradoxical agitation especially in Old age ?? oral, IV, spray midaz, oral diazepam .Lorazepam Sublingual – midaz can be used OTHER DRUGS Oxazepam Temazepam Triazolam Alprazolam ANTIHISTAMINICS (H1) Sedation Anticholinergic Antiemetic Diphenhydramine – oral dose of 50 mg OPIOIDS Previous Morphine and pethidine IM Now fentanyl IV OPIOIDS ++ AND --- Where we need analgesia Ortho IV and arterial lines Decrease anaesthetic requirements But respiratory depression, Sphincter of Oddi, PONV – problems ANTISIALOGOGUES Popular in ether days Now only in Ketamine Fibreoptic intubation REDUCTION IN VAGAL RELEXES (CLINICAL SCENARIO) Traction of ocular muscles Second dose of scoline Propofol, fentanyl, halothane Atropine and glyco pyrollate But – problems central anticholinergic syndrome, tachycardia, blocking sweat glands ?? ADRENERGIC AGONISTS Clonidine in doses of 2.5 to 5 µg/kg – oral sedation, prevent hypertension and tachycardia from endotracheal intubation and surgical stimulation Hypotensive anaesthesia IM,IV – OK ASPIRATION pH of 2.5 and a volume of 25 ml Danger zone Ranitidine , famotidine, nizatidine are H2 blockers ANTACIDS Nonparticulate antacid 0.3 M sodium citrate Colloid antacid suspension Immediate , no lag time Increase volume, with food ?? OMEPRAZOLE Intravenous doses of 40 mg 30 minutes before induction have been used. Oral doses of 40 to 80 mg must be given 2 to 4 hours before surgery to be effective Other PPIs – used GASTROKINETIC AGENTS Gastrokinetic agents are useful because of their effectiveness in reducing gastric fluid volume. Metoclopramide Increased gastric emptying – but no guaranteed emptiness of stomach Antiemetic No change in pH AT THE END ?? ANTIEMESIS Many anesthesiologists prefer not to administer antiemetics as part of a preoperative regimen, but believe that antiemetics should be administered intravenously just before they are needed at the conclusion of surgery. Droperidol, metoclopramide, ondansetron, and dexamethasone PROMETHAZINE Sedation Anxiolysis Antiemesis Alpha blocker Anticholinergic THEY ARE NOT PREMEDICANTS IN STRICT SENSE BUT WE USE Steroids Antibiotics Insulin Methadone ANTIBIOTICS Infective endocarditis prophylaxis Probable contamination Immunosupressed Diabetic On steroids Cephalosporin –ok around one hour prior Vancomycin 2 hours prior Tourniquet !! Give antibiotics before inflation STEROIDS consider treatment in any patient who has received corticosteroid therapy for at least 1 month in the past 6 to 12 months. 80 mg 6 hourly Why ?? 300 mg / day – maximal daily production to stress OTHER PREMEDICANTS TO CONTINUE Beta blockers Thyroxine Statins And the other dugs he /she is taking for systemic illness DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS Heparin Warfarin Clopidogrel When to use and stop – guidelines are there IN A CHILD ?? parental presence on induction of anesthesia an increase in heart rate and skin conductance levels in mothers Oral midaz better than parent and the combined is not very superior IV midaz – wait for 4.8 minutes Intranasal – 10 minutes BENZODIAZEPINES IN PAEDIATRICS Lorazepam slow onset and offset of action, and therefore is better used for inpatients Diazepam immature liver function that would lead to a prolonged half life PEDIATRIC VS. ADULT PATIENTS Vagolysis Anticholinergic Anxiolysis Oral/ nasal/SL routes IM ?? PEDIATRICS Upto 6 months – no problem in parental separation 6 months to 5 years -- maximal psychological problem and anxiety 5 years and above – easy to convince DEXMED PREMED Intranasal dexmedetomidine produces more sedation than oral midazolam when children were separated from their parents and at induction of anesthesia KETAMINE Nasal transmucosal ketamine at a dose of 6 mg/kg is also effective in sedating children within 20 to 40 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Oral ketamine, IM ketamine , IV ketamine PATCHES FOR VENIPUNCTURE EMLA cream (eutectic mixture of local anesthetic), is a mixture of two local anesthetics (2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine). ELA-Max (4% lidocaine) , Ametop (4% tetracaine ) The S-Caine Patch (eutectic mixture of lignocaine and tetracaine – 70 mg of each drug/ patch ) SUMMARY Goals Factors Route Drugs -- benzo, opioids, anticholinergics, promethazine, clonidine, aspiration,antiemetics others Paediatric Thank you all