* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 35Final Review I
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
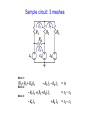
5/19/03 Minute Paper • If a piezo-electric motor can expand and contract with voltage, can it also produce a voltage when it is expanded or contracted? • Is the review going to go through each chapter or are we just going to ask questions and you answer them? Is there going to be any material on the final that will test us on how to use tools that we used in the lab (oscilliscope, multimeter, etc.) • How is current generated by the rotor blades while flight? This happens in a greater magnitude on humid day and when they fly over the ocean, why? Topic 1: DC & AC Circuit Analyses • KCL, KVL: mesh or nodal analyses. Work for both dc and ac circuit. In ac circuits, use impedance and phasor. • Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuit. • Transient circuits: charging and discharging Capacitors • AC power: average and instantaneous (complex) power, power factor, power factor correction. • Three Phase power: structure and advantages Mesh Analysis Example: 2 meshes Step 1: Assignment of mesh currents (clockwise) (mesh is a loop that does not contain other loop). Step 2: Apply KVL to each mesh • • • • The so-called self-resistance is the effective resistance of the resistors in series within a mesh. The mutual resistance is the resistance that the mesh has in common with the neighboring mesh. To write the mesh equation in standard form, evaluate the self-resistance, then multiply by the mesh current. This will have units of voltage. From that, subtract the product of the mutual resistance and the current from the neighboring mesh for each such neighbor. Equate the result above to the driving voltage, taken to be positive if its polarity tends to push current in the same direction as the assigned mesh current. Mesh 1 (R1+R2)I1 Mesh 2 - R2I1 Step 3: Solve currents - R2I2 (R2+R3)I2 = e1 - e2 = e2 – e3 Sample circuit: 3 meshes Mesh 1: Mesh 2: Mesh 3: Mesh Analysis with Current Source i2 I S ( R1 R2 )i1 R2i2 VS i1 i2 i1 VS R2i2 VS R2 I s R1 R2 R1 R2 Example 1 b.In the circuit at right, find the value of Is that will reduce the voltage across the 4 ohm resistor to zero. What if the 2 ohm and 6 ohm are interchanged? 12i1 4i2 10 i1 10 / 8 1.25 A i2 I S I S 1.25 A i1 i2 0 12i1 4i2 10 i2 I S i1 i2 0 Example 2: Ex.2: Which of the two circuits has the larger terminal voltage: A or B? Which of the two circuits has the larger current through the 9 V battery: A or B? Circuit A Circuit B Terminal voltage 1.64 V 1.10 V Current through 9V battery 0.41 A -0.56 A 18.6i1 0.6i2 9 1.5 7.5 18.6i1 0.6i2 9 1.5 10.5 0.6i1 10.6i2 1.5V 0.6i1 10.6i2 1.5V terminal voltage : 9 0.4118 1.64V terminal voltage : 0.56 18 9 1.10V Thévenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits Thévenin Equivalent Circuit Norton Equivalent Circuit How do we calculate RT, VT, iN, RN? Calculation of RT and RN • RT=RN, same calculation • Setting all sources to be zero (“killing” the sources) – Voltage source: short – Current source: open • Calculate equivalent resistance seen by the load. Calculation of VT Remove the load and calculate the open circuit voltage Calculation of IN short the load and calculate the short circuit voltage R1 R2 i1 R2iSC vS R2i1 R1 R2 iSC 0 vS v v v R1 R2 R3 iN iSC vS R2 R1R3 R2 R3 R1R2