* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measurement and technology
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
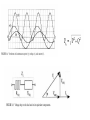
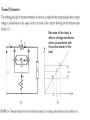
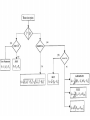
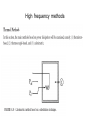
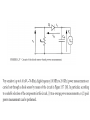
Measurement and technology II. Electric power measurement current division voltage division Instantaneous power: depending on time Active power: The time average of the intantaneous power. It gives amount of dissipated energy Effective values! Apparent power Reactive power P/P_A called power factor, cos(fi) The above has presented the power definitions applied to ac circuits with the restrictions of sinusoidal quantities. In the most general case of distorted quantities, obviously symbolic representation can no longer be applied. In any case, active power is always defined as the mean power dissipated in one period. As far as methods and instruments for ac power measurements are concerned, some circuit classification is required. In fact, the problems are different, arising in circuits as the frequency of power supply increases. Therefore, in the following, ac circuits will be classified into (1) line-frequency circuits, (2) lowand medium-frequency circuits (up to a few megahertz), (3) and (3) high-frequency circuits (up to a few gigahertz). Line-frequency circuits: related specifically to the three-phase power supply Three voltmeter method Because of the load, a delta e voltage imbalance arises proportional with the active power of the load Wattmeters Based on Multipliers The multiplication and averaging processes (Figure 3.8) involved in power measurements can be undertaken by electronic means. Electronic wattmeters fall into two categories: analog (continous) or discrete In continuous methods, multiplications are mainly carried out by means of analog electronic multipliers. In discrete methods, sampling wattmeters take simultaneous samples of voltage and current waveforms, digitize these values, and provide multiplication and averaging using digital techniques. Errors: 1. resistances of the voltage and current circuits have to be taken into account 2. phase errors of both current and voltage circuits increase the relative uncertainty of power measurement, 3. sinusoidal conditions. The main analog multipliers are based on a transistor-based popular circuit such as Four-quadrant multiplier [3], which processes voltage and current to give the instantaneous power, and an integrator to provide the mean power (Figure 3.9) Time Division Multipliers (TDMs) Hall effect-based multipliers. Discrete utilities Approx. periodic time synchronous sampling Line applications Result: sum of P1,P2,P3 High frequency methods Pulse power measurement