* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Adult neurogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hippocampus wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
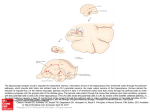
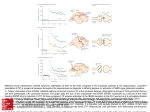
The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the direction of impulse flow.) In the indirect trisynaptic pathway neurons in layer II of entorhinal cortex send their axons through the perforant path to make excitatory synapses onto the granule cells of the dentate gyrus. The granule cells project through the mossy fiber pathway and make excitatory synapses with the pyramidal cells in area CA3 of the hippocampus. The CA3 cells excite the pyramidal cells in CA1 by means of the Schaffer collateral pathway. In the direct pathway neurons in layer III of entorhinal cortex project through the perforant path to make excitatory synapses on the distal dendrites of CA1 Source: Prefrontal Cortex, Hippocampus, and the Biology of Explicit Memory Storage, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon pyramidal neurons without intervening synapses. Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 13, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved