* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide () - AccessEmergency Medicine
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Index of biochemistry articles wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
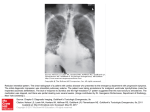
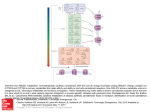
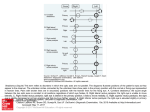
Botulinum toxins consist of two peptides linked by disulfide bonds. The heavy chain is responsible for specific binding to acetylcholine (ACh) containing neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the nerve cell cytoplasm. The light chain contains a zinc-requiring endopeptidase that cleaves soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor (NSF) attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins belonging to the docking/fusion complex required for neuroexocytosis of ACh. These proteins may be associated with the synaptic vesicles (v-SNARE) or with their targets on the presynaptic membrane (t-SNARE). Botulinum toxin types A and E proteolyse the t-SNARE protein known as synaptosomal-associated protein (SNAP)-25, and BoNT type E cleaves both SNAP-25 and syntaxin, which is attached to SNAP-25 and to the Source: Botulism, Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies, 10e presynaptic membrane. BoNT types B, D, F, and G target the v-SNARE protein synaptobrevin. As a result of cleavage of these components of the docking Citation: Hoffman RS, M, Lewin NA, Nelson LS, Goldfrank LR. Goldfrank's complex by the endopeptidase, AChHowland is not released and neuromuscular transmission is impaired.Toxicologic Emergencies, 10e; 2015 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 12, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved