* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture-5 - Dr. Imtiaz Hussain
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
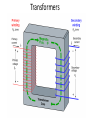
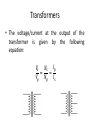
Electronic workshop Lecture-5 Inductors and Transformers Dr. Imtiaz Hussain email: [email protected] URL :http://imtiazhussainkalwar.weebly.com/ Inductors • Generally - coil of conducting wire – Usually wrapped around a solid core. If no core is used, then the inductor is said to have an ‘air core’. Symbols Inductors • Values specified in henries (H), millihenries (mH) and microhenries (μH). • Inductor can be fixed value or variable. Fixed Value Inductor Variable Inductor 4 Inductor types Molded inductor & air-wound inductor Ferrite core toroidal transformer Adjustable air-wound inductor Air wound inductor Iron powder toroidal inductor 5 Inductor ratings • Wire gauge and physical size of the coil determine the current handling capacity. • Core material dependence. will have a temperature • Air is best, followed by iron powder, then ferrites. 6 Inductor handling • Inductors are not polarized and may be installed in either direction. • Mechanical stress due to lead bending should be minimized. • Inductors in timing or frequency determining circuits should be installed in a mechanically rigid fashion. 7 Color Coding Inductor Applications • Speakers • Solenoid Valves • Resonant Circuits Task#1 • An ideal inductor would exhibit zero resistance but a real inductor has some finite resistance. • Inductors which have become open will show infinite resistance, whereas shorted inductors will show a resistance of zero Ohms. • Take few resistors and check them for any faults. Transformers • A transformer is a device that uses a pair of coils/windings to manipulate AC voltage and current. • It uses the principle of mutual induction to either decrease or increase the voltage/current at its input. Transformers Transformers • The voltage/current at the output of the transformer is given by the following equation: 𝑉𝑠 𝑁𝑠 𝐼𝑝 = = 𝑉𝑝 𝑁𝑝 𝐼𝑠 Task#2 S N.o 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Peak to Peak Input Voltage Output Voltage Turn Ratio To download this lecture visit http://imtiazhussainkalwar.weebly.com/ END OF LECTURE-5