* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diode Rectifiers
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
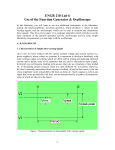
Student Name __________________________ Diode Rectifiers D VAC R CH1 CH2 Equipment: An AC signal generator - VAC An Oscilloscope Leads A 1N4001 rectifier diode A 2.2 kΩ resistor Procedure: 1. Connect the components as shown on the diagram above. Initially it is sufficient to connect only channel 1 of the oscilloscope. 2. Adjust the signal generator to produce a 5 volt rms sine wave output at a frequency of 500 Hz. You can check the rms output voltage from the signal generator using a DMM. 3. Adjust the oscilloscope to obtain a stable display of the CH1 voltage waveform and sketch this to scale on the results sheet. 4. Use the oscilloscope display to measure the peak amplitude and the period of the signal generator output voltage. Convert the peak voltage value to rms and compare the measurements with the expected values of voltage and time. Do you think that the oscilloscope voltage measurement is better or worse than that from the DMM? Explain. 5. Use the measured value for the period of the waveform to calculate the frequency of the signal generator output. 6. Set the oscilloscope to display the CH2 voltage waveform and sketch this to scale on the results sheet. 7. Explain why the voltage measured across resistor R is said to be half wave rectified. 8. Measure the difference between the positive peak voltage on CH2 and that on CH1. Explain the difference. Student Name __________________________ 9. Disconnect the diode D and instead connect the bridge rectifier module between VAC and R. 10. Measure and sketch the new voltage waveform across R to scale. Comment on the peak value of the new voltage waveform. 11. Suggest a reason why the bridge rectifier output voltage might be considered an improvement on the output from the half wave rectifier. Student Name __________________________ Step 3 Voltage Waveforms: CH1 Volts per Division ___________ CH2 Volts per Division ___________ Time per Division ___________ Step 4: Peak Amplitude __________________________________ Period __________________________________________ RMS Amplitude __________________________________ Student Name __________________________ Step 5: Frequency = 1/Period = __________________________________________ Step 6: CH1 Volts per Division ___________ CH2 Volts per Division ___________ Time per Division ___________ Student Name __________________________ Step 7: Step 8: Voltage difference = ________________________ Step 10: CH1 Volts per Division ___________ CH2 Volts per Division ___________ Time per Division ___________ Student Name __________________________ Comment: Step 11: