* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 7 Objective A
Survey
Document related concepts
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
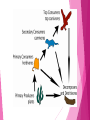
Unit 7 Objective A ECOLOGY Vocabulary Community Group of various species that live in the same place and interact with each other Ecosystem The group of species along with the living and nonliving environment Biotic Factors Bio means… Biotic factors are the relationship between living organisms in an ecosystem Humans pick flowers Coyotes eat chickens Abiotic factors A means…. Bio means… Abiotic factors are physical or nonliving factors of an ecosystem Oxygen, water, sunlight, temperature, rocks, climate, buildings Tropical rainforests have lots of different plants and animals Tropical rainforests have plenty of water to drink, food to eat, places to live/hide Habitat The place where an organism lives Biodiversity Bio means… Diversity means…. Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms in a given area Affected by abiotic factors Extreme temperatures Limited water Limited food Affected by biotic factors Predators Human habitat destruction Biodiversity High biodiversity Ecosystem Better that is healthy able to resist change (disaster) Low biodiversity Ecosystem NOT that is Unhealthy able to resist change (disaster) Ecosystem can crash Succession What happens after a disaster?? Replacement of one community by another at a single place over a period of time Pioneer species First species to appear in a newly made habitat Help break down the damage so that other species may grow Pioneer species is then replaced by next generation Succession • Major change in ecosystem – Volcano, glacier receding, etc. • Ecosystem is destroyed • Pioneer species take root in new ecosystem. – Begins the restoration of damaged ecosystem • Pioneer species is then replaced by new species • That new species is then replaced and so on Succession Succession Equilibrium • A condition which results in a stable, balanced, or unchanging system • After damage work towards equilibrium Climate • Two key factors of climate – Temperature • Animals usually live within a certain range of temperatures – Precipitation • Amount of precipitation determines the amount of water available for organisms • Little water means few organisms Trophic Levels One of the steps in a food chain Refers to the transfer of energy when 1 organism consumes another Trophic Levels Producers AUTOTROPHS - produce their own food Consumers HETEROTROPHS Decomposers – consume their food Food Chains The FIRST level is PRODUCERS The SECOND level is CONSUMERS Primary Consumer Herbivores eat the carbohydrates the producers produced The THIRD level is CONSUMERS Secondary Consumer Small Carnivores Animals that eat herbivores Animals that eat other animals They take energy from the sun and convert it into carbohydrates They “produce” food The FOURTH level is CONSUMERS Tertiary Consumer Large Carnivores Animals that eat other carnivores Food Web Animals eat more than 1 kind of food We use food webs to illustrate these complicated interactions 10% Rule Of the 100% of food we eat… 90% is given off as heat, digested, excreted, etc. 10% is kept within our bodies (growth) Producer – Plant Consumer – Herbivore 10% passed on 10% passed on Consumer - Carnivore Ten Percent Rule Energy Pyramid