* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.2 - Measuring Segments
Foundations of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Musical notation wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard analysis wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
John Wallis wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Homogeneous coordinates wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
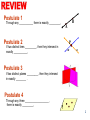
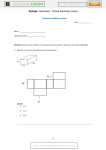
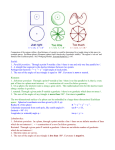
1.2 measuring segments Postulate 1 Through any ___________ there is exactly _________. Postulate 2 If two distinct lines _________, then they intersect in exactly ___________. B A P m n Postulate 3 If two distinct planes _________, then they intersect in exactly ________ . Postulate 4 Through any three ___________________ , there is exactly _________. 2 • Every point on a __________________________________. • The real numbers that corresponds to a point is called ______________________ . • The _________ between any two points on a number line is the ___________ of the ____________ of the real numbers corresponding to the points. Formula: Take the ________________________of the two coordinates a and b: 3 Find the distance between P and K. G H I J K L M N O P -5 Q R S 5 Therefore, the coordinates of points P and K are and respectively. Substituting the coordinates in the formula PK = Remember : Distance is always positive 4 Congruent Foot Example vs. Equal = Example B CB CAB ACB AB R 10 m 70° A 10 m AB = 10 m CB = 10 m mCAB = 70° mACB = 70° 70° C Definition: ___________________________. (congruent symbol: ) B A Congruent segments can be marked with _______ . C D If numbers are ______ the objects are __________. AB: the segment AB ( an object ) AB: the distance from A to B ( a number ) Correct notation: AB = CD AB CD Incorrect notation: AB CD AB = CD 8 A B C Example: If AC = x , CB = 2x and AB = 12, then, find x, AC and CB. A C B 10