* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MUSCARINIC RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS:
Discovery and development of tubulin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
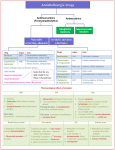
MUSCARINIC RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS: General Uses: 1. To produce mydriasis (dilated pupils). 2. To treat COPD. 3. To treat smooth muscle spasma (associated with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence). Classes: A. Naturally Occurring alkaloids and smisynthetic derivatives Drug 1. Atropine – a natural product. S-enantiomer is the active form aka HYOSCAMINE, w/c is a therapeutic agent in itself. 2. Scopolamine Description 3. Ipratropium – similar potency as atropin 4. Tiotropium Tx Application Tropine based. Contains bulky ester grp., which contributes to antagonist action. HYOSCAMINE – the active form. An antidote for AChE inhibitor poisoning. 3,tiary amine Greater CNS action than atropine. Easily cross the blood/brain barrier Active S-enantiomer. Contains and epoxide grp. Natural derivative of atropine Atropine derivative. A 4’nary N which leads to poor absorption of swallowed dose, therefore minimizing the systemic effects. a scopolamine derivative. Same therapeutic /pharmacologic profile as ipatropium contains synthetic ester ( a Thiophene ring) Precautions/ Side effects Cardiac stimulant effect To treat muscarine (mushroom) poisoning Combined with an opioid (Lomotil) for diarrhea Nerve gas poisoning HOMOTROPINE – shorter duration and is useful in eye exam Transderm scope for motion sickness COPD by inhalation Local axn in the lung COPD use once daily Asthma (less effect on lung secretion) Duration 0.5 mg - dry mouth & skin 1.0 mg - Increased heart rate, thirst. 2 mg - pupillary dilation, blurred vision tachycardia 5 mg – Reduced peristalsis, urinary retention, hot dry skin, fatigue, flushing 10 mg - Rapid and weak pulse, ataxia, hallucinations, delirium, coma Amnesia Sedation Stupor and hallucinations (Criminally abused to render victims compliant) Long: 7-10 days 90 % of the drug is swallowed (very inefficient) Several days Longer acting than 3. B. Tertiary Amines Muscarinic Antagonists: functional selectivity for the urinary bladder. All are orally available and are typically absorbed well. Drug Description 1. Oxybutynin 2. Tolderodine 3. Solifenacin Tx Application Undergoes CYP3a4-Ndeethylation giving an active metabolite (happens at 1st –pass metabolism) Yields an active metabolite, a hydroxtmethyl metabolite, which have the similar activity as the parent drug. Single R-enantiomer, not racemic urinary incontinence bladder hyper irritability Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder Single enantiomer – 2 chiral center Overactive bladder Precautions/ Side-effects / Metabolism Duration Ketoconazole is a 3A4 inhibitor – AUC will increase and so as S/E. If this happens, oxybutynin dose should be lowered. Metabolism: Cyp2D6 is the major p/w yielding active metabolite. (genetic polymorphism – 70 % of pop’n are poor metabolizers Cyp3A4 is the minor p/s Active N-dealkylation Metabolsm: Cyp3a4: Yeilds N-oxide and 4Rhydorxy metabolite but these metabolites don’t contribute to activity. 4R-hydroxy could be active but its [c] is not enough for activity 45-68 hrs. Dosing is once daily C: Quaternary Ammonium Muscarinic Antagonists: Drug Glycopyrrolate Trospium Description For pediatric patients Tx Application Precautions/ Side-effects Overactive bladder Overactive bladder Duration 20 hrs D. Antimuscarinic Antiparkinsonian Agents: Should be lipophilic, contains 3’tiary amine, and highly polarity to access/penetrate the CNS Drug 1. Benztropine 2. Procyclidine Description Has 3’tiary amines Highly lipophilic Has 3’tiary Alohol Contains aromatic ring (makes the alcohol greasy) Tx Application Duh!!! Use in eye exams for papillary dilation and treatment of iritis Precautions/ Side-effects Duration E: Amine Muscarinic Antagonists: 1. Tropicamide Shorter duration of action than atropine 6 hrs