* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download igneous rocks
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
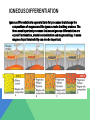
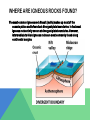
TYPES OF ROCK If an igneous rock is intrusive (plutonic) that means it formed and cooled under the Earth’s surface (crust) and since the temperatures are greater at this level the rocks would take longer to cool. If an igneous rock is extrusive (volcanic) that means it formed on or close to the Earth’s surface where temperatures are cooler than deep within the earth. This would give the igneous rock samples small or possibly no crystal structure at all. ROCK EXAMPLES intrusive igneous rocks: diorite, gabbro, granite and pegmatite . extrusive igneous rocks: andesite, basalt, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite and scoria. Obsidian Scoria Pumice GEOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE their minerals and global chemistry give information about the composition of the mantle, from which some igneous rocks are extracted. their absolute ages can be obtained from various forms of radiometric dating and thus can be compared to adjacent geological strata. their features are usually characteristic of a specific tectonic environment, allowing tectonic reconstitutions. Igneous rocks help us determine if there is or was thermal activity going on inside the rocks layers. CLASSIFICATION Igneous rocks are classified according to mode of occurrence, texture, mineralogy, chemical composition, and the geometry of the igneous body. Two important variables used for the classification of igneous rocks are particle size, which largely depends on the cooling history, and the mineral composition of the rock. In a simplified classification, igneous rock types are separated on the basis of the type of feldspar present, the presence or absence of quartz. IGNEOUS DIFFERENTIATION Igneous differentiation is a general term for processes that change the compositions of magmas and the igneous rocks that they produce. The three most important processes that cause igneous differentiation are crystal fractionation, crustal contamination and magma mixing. In some magmas liquid immiscibility can also be important. WHERE ARE IGNEOUS ROCKS FOUND? The most common igneous rock Basalt (mafic) makes up most of the oceanic plates and is founds at divergent plate boundaries. In fact most igneous rock activity occurs at divergent plate boundaries. However, intermediate to felsic igneous rocks are most commonly found along continental margins.