* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
The Weather Channel wikipedia , lookup
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
Water vapor wikipedia , lookup
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Convective storm detection wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Weather Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
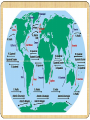
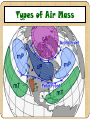
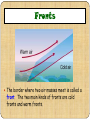
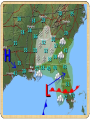
Chapter 3 Weather Lesson 2 How do the ocean and Water Cycle affect weather? current weather humidity precipitation Current Water on the ocean surface is pushed forward by winds. The result is a current or a stream of water that flows like a river through the ocean. Ocean Affect Weather The oceans help keep Earth’s weather mild. The temperature on Earth would be much more extreme without oceans. Ocean Affect Weather During the summer, the oceans absorb much heat from the sun. This absorption keeps the air over the ocean cooler. In the winter, the ocean release heat into the air above them, causing the planet to be warmer. Water Cycle The constant movement of water from the Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to the earth’s surface. Weather Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place. What you may call weather is the water cycle at work. Humidity Some areas of the atmosphere have more water vapor than others. The amount of water vapor in the air is called humidity. Humidity A large amount of water vapor is high humidity. A small amount of water vapor is low humidity. Humidity depends on partly the airs’ temperature. This is a hygrometer. It measure the amount of water vapor, or humidity in the air. Warm air has more water vapor in the air in it than cold air. High humidity usually means its about to rain. Georgia Humidity Map Cloud Formation Clouds form in air that is high in humidity, or water vapor. As warm air is forced up, it cools. Some of the water vapor begins to condense on bits of dust and other particles in the air. As more and more water condenses, a cloud forms. Types of Clouds Cumulus very puffy fair or good weather, if they are gray at the bottom, rain may come. Stratus form low in atmosphere. look long and flat Usually mean some rainfall or snow is coming. Cirrus form high in atmosphere where the air is very cold. Made mostly of ice crystals. Cloud Formation What type of clouds are in the pictures above? Precipitation Rain Sleet Snow Hail Let’s Review How does the ocean affect temperature and weather? What causes clouds to form? Describe each type of cloud. What is a current? What does humidity tell you about the weather? Lesson 3 How is weather predicted? Vocabulary meteorology barometer anemometer hygrometer Air mass front climate Meteorology The study of weather is meteorology. To study weather, scientist must first measure it. Meteorologist, scientist who study weather, use many measuring instruments. Weather Instruments Thermometer Barometer Measures air pressure which Measures air temperature. If the air cools down during the day or warms up in the evening, this change may mean rain is coming. is also called barometric pressure. A change in the air pressure often means the weather is about to change. Weather Instruments Anemometer Hygrometer Measures humidity, or water Measures the wind speed. A change in wind speed may mean the weather is about to change. vapor. An increase in humidity often means its about to rain. Air Mass An air mass is a large body of air that has the same temperature and humidity throughout. Air masses can be warm, cold, humid, or dry. The type of air mass is based on the region where it forms. Types of Air Mass There are four kinds of air masses that affect weather in the United States. Continental Polar (cP) bring cool and dry weather. Maritime Polar (mP) bring cold and humid weather. Continental Tropical (cT) bring hot and dry weather. Maritime Tropical (mT) bring warm and humid weather. Types of Air Mass Fronts The border where two air masses meet is called a front. The two main kinds of fronts are cold fronts and warm fronts. Warm Fronts A warm front forms where a warm air mass moves over a cold air mass. It get warmer and more humid after a warm front passes. It brings rain or snow that last for hours. Cold Fronts A cold front forms when a cold air mass moves under a warm air mass. It gets cooler and drier after a cold front passes. It brings heavy rain or snow that will pass quickly. Weather Maps A weather map gives you information about what the weather is like in an area. Weather Map Symbols Rainy Weather Sunny Weather Partly Cloudy H High Pressure L Low Pressure Cold Front Warm Front Let’s Review How can weather be predicted? Name and describe each type of weather instrument. What is the difference between air mass and a front? What kind of information is given on a weather map? Identify following symbols from a weather map. L H