* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advertising Campaign
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Advertising wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Audience measurement wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
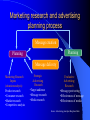
Advertising Campaign Uma Kanjilal Promotional Mix It is the combination of individual promotional tools selected by the marketer to promote a particular product. Tools for promotional mix Advertising Personal selling Sales promotion Publicity and public relation Direct marketing Advertising Any paid form of non-personal communication link, initiated by an identified marketer, to establish or continue exchange relationship with customers and other stakeholders. Advantages of Advertising Low cost per target audience reach Repetition of message Dramatization of company and its products for creating impact Build up long-term image Disadvantages of Advertising High absolute cost Difficult to evaluate effectiveness Persuasive value less compared to other personal promotional tools Types of Advertising Product Advertising- focuses on goods and services Institutional advertising- focuses on the organization, generating a particular image or concept Individual Advertising Categories Pioneering advertising- to introduce a new product or brand Reminder advertising- keeps the name of the marketer in front of the target market Competitive advertising- stressing superiority of one product over the other Comparative advertising- superiority over the competing brand Advocacy advertising- to communicate marketers position on an issue Public service advertising- ads by government or other non-profit organizations on social issues. Advertising process Review internal/external strategies and plans Identify target audience Set advertising objectives and budget Develop creative approach Conduct advertising research Selecting media Producing advertising Evaluation Personal selling Interpersonal communication process used to identify prospects, determine needs, present product information, gain commitment and follow up after sales to maintain customer relationship. Personal selling types Telephone selling Technical selling- providing technical support Missionary (pioneer) selling- providing details about the product Retail selling Methods of Personal Selling Field sales- sales calls made at customer’s home or business locations Over the counter sales- sales at retail or wholesale locations when customers visit there Telemarketing- contact through telephone Advantages of Personal Selling Two way communication with target audience Immediate feedback Flexibility in responding to individual customer needs Customer relationship building Disadvantages Cost per customer contact high People dependent method Sales promotion Communication of any intermittent and/or short-term incentive that enhances the basic value of a product, to encourage channel members and sales people to market it and customer to buy it. Categories of Sales promotion Consumer sales promotion- range of promotional incentives that marketers offer to ultimate consumers to encourage purchases Trade sales promotion- promotional incentives offered by marketers to wholesalers, retailers and other value chain partners for supporting certain products Types of consumer sales promotion Coupons- a document that allows customer to buy a product at a specific discount Samples- goods or service offered free or at a very low price to encourage the customer the experience its benefits Sweepstakes and contests- these are ways to attract new customers premium- item of value offered free or at a low price to customers to buy or try a particular product. Types of consumer sales promotion… cont. Price promotion- price reduction offered to every purchaser during a limited period refunds and rebates- these method the marketer encourages the customer to take a risk. Full or partial refunds are made if they are not satisfied Displays- in-store displays and point-of-purchase displays are set up in retail outlets to grab customer attention. Trade sales promotion Trade allowances- off-invoice allowance, extra allotments for buying a minimum quantity are some of the methods used to wholesalers and retailers. Incentives and contests- push money (cash awards) to sales persons for selling certain products, contests in B2B marketing to whip up enthusiasm for a certain product Marketing communication strategies … cont. Step 4- Identify competitive consumer benefit (key benefit that makes the product better than competing brand) Step 5- Communicate the truth of the benefit (product attributes, consumer perception supported, believable messages) Step 5-Convey the brand personality (decide on the tone and personality that differentiates the product from others Marketing communication strategies … cont. Step 6- Develop communication objectives (state what consumers should know and feel and what they are expected to do after they are exposed to the message Step 7- Plan consumer contact points (know when and where the consumer will be most receptive to the message) Strategic advertising research Target audience analysis- who the audience are, their characteristics, and their consumption and media habits Message research- concept testing, copy testing Media audience research- broadcast audience measurement, print audience measurement Marketing research and advertising planning process Message creation Planning Planning Message delivery Marketing Research Inputs (situation analysis) Product research •Consumer research •Market research •Competitive analysis Strategic Advertising Research •Target audience •Message research •Media research Evaluative Advertising Research •Message post testing •Effectiveness of message •Effectiveness of media Source: Advertising principles/ Bergh and Katz Research decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Should research be done? What is the research objective? What research design will provide best solutions? What data collection methods to be adopted? What conclusions to arrive at with analyzed research data? Strategic planning for advertising and marketing communication Determining objectives or outcomes expected developing strategies that are plans for accomplishing the set objectives Adverting and marketing communications objectives Selecting a target market- market segmentation (undifferentiated, differentiated or concentrated market segmentation strategies) Setting objectives Criteria for setting objectives Identify unit responsibility Link objectives State output not input Establish a time frame Set realistic objectives Include result per objective Make objective specific and measurable Media planning process Advertising factors - Budgeting - Competitive activity - Media usage - Message types/ approaches - Organization - Research - Target audience Media planning factors - competitive spending analysis - Geographic distribution - Media goals - Media mix - Seasonality - Target audience - Timing


















































![5-02 Advertising Procedures [June 17, 2015]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000164077_1-2701ac7a4045d9309a79a5a64725d9ac-150x150.png)


