* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download g-protein-coupled-receptor-presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
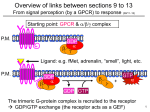
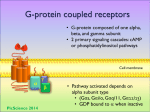
G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTOR REBECCA BEBE, JORDAN BELGRVE, ALEXIS CAREY, TAMARA DUNFORD, HASAN STOCKTON, JESSICA VASON, ETURNITEE WALKER G-PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTOR • Found only in Eukaryotes • Largest known class of membrane receptors • Humans have over 1,000 • Each one has a specific function KEY NOTES • Has 7 transmembrane α-helixes-spans the membrane 7 times • All associated G-proteins are have three subunits • Subunits making up the G- protein include: • α-subunit (attatched to membrane) • β-subunit • γ-subunit (attached to membrane) • When inactive: GDP is bound to the alpha subunit • When active: GTP is bound to the alpha subunit FUNCTION OF GPCR • Ligand shape is complementary to that of the GPCR for binding • When bound together GPCR changes conformation • α-subunit exchanges GDP for GTP • α-subunit separates from β-subunit and γ-subunit (dimer) • α-subunit regulates function of target protein • Target protein sends signal FUNCTION OF TARGET PROTEIN • Target protein converts ATP to cAMP • cAMP sends signal to other cells • Process breaks gown glycogen forming glucose AFTER THE SIGNAL HAS BEEN SENT • GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP • Subunits recombine • GCPR looses ligand and returns to original conformation