* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adaptation and Speciation
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
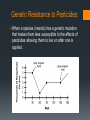
Speciation and Adaptation Warm-up Questions: • Some organisms have genes that improve their ability to survive and reproduce. If the genes also help their offspring survive and reproduce, then which of the following will most likely increase? • • • • a. b. c. d. The frequency of the genes in one individual The frequency of the genes in the population The number of genes in one chromosome The number of genes in the species • Identify the type of selection displayed in the graph below: Stabilizing Inherited Variation: Variation in a characteristic that is a result of genetic inheritance. Essential for natural selection to result in a new species. Advantageous Adaptation: An adaptation that is beneficial to the organism (physical adaptations, or even changes in breeding to produce when food is most heavily available.). Adapted for an environment with bright light. Fitness: In evolutionary terms, fitness is the an organism’s reproductive success in surviving and producing viable offspring. Genetic Resistance to Pesticides: When a species (insects) has a genetic mutation that makes them less susceptible to the effects of pesticides allowing them to live on after one is applied. Speciation: The formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution. The start of a new population elsewhere often provides the best opportunity for speciation to occur. Recombination: Process by which pieces of DNA are broken and recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms. Gene Frequency: The ratio of a particular allele to the total of all other alleles of the same gene in a given population. Differential Reproductive Success: The difference between individuals in a given generation and how many offspring they are able to leave. The more successful the adaptions, the more likely an organism is to have a greater amount of offspring. To improve success, some species produce more babies than will survive in order to maintain a steady population. Mimicry: Mimicry is a similarity of one species to another that protects one or both. Example: A scarlet king snake, though harmless, mimics the pattern if the venomous coral snake in order to deter predators. Venomous Non-venomous