* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Product Life Cycle
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
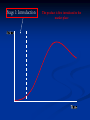
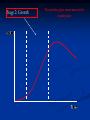
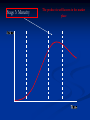
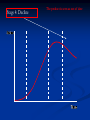
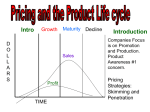
The Product Life Cycle Stage 1: Introduction The product is first introduced to the market place Stage 1: Introduction Increasing high costs - little revenue / low economies of scale High marketing expenditure – increase product awareness Low sales – Customer awareness is low High risk – Will the market accept it? Competition - New product noticed by competitors Price policy – Skimming or penetrating Stage 2: Growth The product gains momentum in the market place Stage 2: Growth Increasing sales volume – Popularity equals more sales Retailers – Wanting to stock the product Profits – Increase Costs – Fall due to economies of scale Competitors – ‘Copycat’ products enter the market Brand loyalty – Attempt made to encourage it Price - Product suffers from rises and falls Stage 3: Maturity The product is well known in the market place Stage 3: Maturity / Saturation Sales - Continue to rise but rate of growth slows Competition – Increases further Marketing – Further needed to maintain market share Rivals – Weaker ones leaving the market Extension strategies – Planning begins Stage 4: Decline The product is seen as out of date Stage 4: Decline Sales – Dramatic fall Competition – Many substitutes available Marketing – Withdrawn Profit - Declines further Product – Withdrawn, seen as damaging to company image Stage 1: Introduction