* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Athero Arteriosclorsis
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
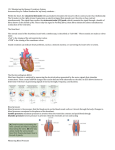
Mayo Clinic in Minnesota has been recognized as one of the top Cardiology & Heart Surgery hospitals in the nation for 2014-2015 by U.S. News & World Report. Arteriosclerosis occurs when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff — sometimes restricting blood flow to your organs and tissues. Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic, but over time, the walls in your arteries can harden, a condition commonly called hardening of the arteries. Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis, but the terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Atherosclerosis refers to the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on your artery walls (plaques), which can restrict blood flow. These plaques can burst, triggering a blood clot. Although atherosclerosis is often considered a heart problem, it can affect arteries anywhere in your body. Atherosclerosis usually is preventable and is treatable. Both can cause heart disease, heart attack and stroke. Cardiology There are two major classes of cardiac fibrillation: atrial fibrillation and ventricular fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of atria. It can be a chronic condition, usually treated with anticoagulation and sometimes with conversion to normal sinus rhythm. In this condition the normal electrical pulses coming from the sinoatrial node are overwhelmed by disorganized electrical impulses usually originating in the roots of the pulmonary veins, leading to irregular conduction of impulses to the ventricles which generate the heartbeat. Ventricular fibrillation is an irregular and uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of ventricles. It is a common cause of cardiac arrest and is usually fatal if not reversed by defibrillation. Fibrillation may sometimes be used after heart surgery to stop the heart from beating while any minor leaks are stitched up.