* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
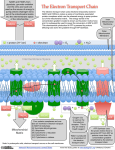
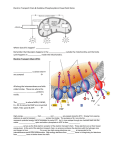
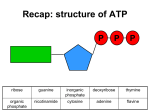
Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain - ETC Interconnected proteins - named by Roman numerals (on large graphic on back of page) - embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane ETC Jobs 1. Dehydrogenases: Removal of H from NADH and FADH Separation into a high energy electron e- & H+ 2. Proton pumps: Energy of e- pump H+ into intermembrane space creating a Hydrogen ion gradient: Chemiosmosis • creates a 100 xH+ concentration difference over inner mitochondrial membrane 3. Low energy e- is unloaded onto oxygen which reacts with H+ to form water (See equation) ½ O2 + 2e- + 2H+ H2O Oxygen is the final electron acceptor of aerobic cellular respiration – this is why you breathe air! Stage 5 Digestion: ATP Synthesis ATP Synthesis • Harvesting energy of the H+ gradient • Works like a water wheel ATP Synthase Enzyme • Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane • allows H+ gradient to rush through using energy to make ATP ADP + P ATP ATP Conversions • 1 cytosolic NADH = 2 ATP • 1 mitochondrial NADH = 3 ATP • 1 mitochondrial FADH = 2 ATP Net ATP from 1 Glucose • 2 ATP (G) • 2 NADH2 (G) = 2 FADH2 (transport) • 2NADH2 (K prep) • 2 x 3 NADH2 (K) • 2 x FADH2 (K) • 2 x 1 GTP (K) Total ATP 2 4 6 18 4 2__ 36 Location? In which cellular compartment does each of the following take place? a. Glycolysis b. Citric Acid Cycle c. Electron Transport Chain d. Hydrogen Ion gradient e. ATP synthase Lipid metabolism • Cytoplasm: lipase separates Glycerol and Fatty Acids • Glycerol (C3) is converted to Pyruvate (C3): yields NADH • Fatty Acids are transported into Mitochondria for β-Oxidation • Chopped into 2 carbon molecules to make Acetyl-CoA • Yield 1 NADH, 1 FADH/chop Amino Acids Liver: Removal of amino group as NH3 (ammonia) Ammonia is toxic, reacts with CO2 to form urea, secreted as liquid waste: kidneys O NH3 + CO2 Ammonia NH2-C-NH2 urea Carbon skeleton of AA • AA skeletons with 2 C → Acetyl • AA skeletons with 3 C →Pyruvate • AA skeletons with 4 C → Succinate fumarate, malate, oxaloacetate • AA skeletons with 5 C→ α-Ketoglutarate