* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forms of Energy
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
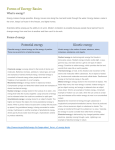
Forms of Energy There are two main forms of energy – potential and kinetic 1. Potential energy is energy that isn't being used yet. It is stored. It is also the energy of position, sometimes called gravitational energy. There are different types of PE a. Chemical PE is stored in bonds between atoms and molecules. When these bonds are broken they release energy as heat, light, motion, and sound. (Ex: coal, oil, propane, and food) b. Elastic PE is stored by something that can stretch. It is found in objects that want to bounce back into their natural shape. (Ex: guitar string and rubber band) c. Nuclear PE is energy which holds together the nucleus of an atom. It is released when atoms are split open (fission) or smashed together (fusion) d. Gravitational PE is energy stored due to height and where it is placed. A roller coaster at the top of its rails has gravitational energy & water held behind a dam's reservoir. 2. Kinetic Energy is energy which is being used. It is the energy of motion. There are different types: a. Electrical KE is caused by the movement of electrons. (Ex. Lightning and electricity in our homes) b. Radiant KE (electromagnetic or light) is energy that comes from the waves of the electromagnetic spectrum. (Ex. Light, x-rays, gamma rays, ultraviolet rays, infrared rays, microwaves, & radio waves) c. Thermal KE is heat. Heat is caused by the movement of atoms and molecules within a substance. Heat moves from warmer to cooler. d. Motion KE (mechanical) is energy caused by objects or substances that are moving. (Ex. Tides & wind) e. Sound KE is caused by vibrations or back-and-forth movements of matter. They can be compressional or longitudinal waves.