* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun and Space Objects
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
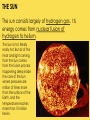
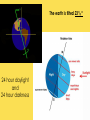
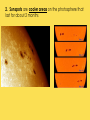
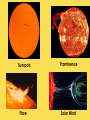
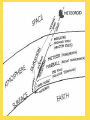
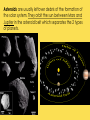
THE SUN The sun consists largely of hydrogen gas. Its energy comes from nuclear fusion of hydrogen to helium. The Sun is hot. Really really hot. But all of the heat and light coming from the Sun comes from the fusion process happening deep inside the core of the Sun where pressures are million of times more than the surface of the Earth, and the temperature reaches more than 15 million Kelvin. The earth is tilted 23½ º 24 hour daylight and 24 hour darkness WHAT CAUSES SEASONS? Earth’s tilt causes seasons Earth revolves around the sun tilted on its axis. The angle at which the sun’s rays strike each part of Earth’s surface changes as Earth moves through its orbit. SOLSTICES 1. Summer Solstice---sun shines the longest on this day…occurs June 22 in the northern hemisphere 2. Winter Solstice---shortest amount of sunlight on this day…occurs December 22 in the northern hemisphere SUMMER WINTER EQUINOXES 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness on equinox days 1. Spring equinox occurs on March 21st in the northern hemisphere 2. Fall equinox occurs on September 21st in the northern hemisphere THE SUN •The largest object in the solar system, in both size and mass •Contains 99% of all the mass in the solar system…made up of hydrogen and helium •109 Earths lined up edge to edge to fit across the Sun •Nothing “solid” about the sun… its interior is plasma —the 4th state of matter…solid, liquid, gas, plasma (ionized gas) Layers of the Sun 1. Photosphere is the visible surface of the Sun 2. Chromosphere is only visible during a solar eclipse or with special filters…appears as a red circle around the sun during the eclipse 3. Corona is only visible during a solar eclipse or with special filters…appears as white glow that extends several million miles into space The Sun’s Activity 1. Solar Wind is an energized gas that flows out from the corona at high speeds. The solar wind is deflected by the earth’s magnetic field, however this is what causes the northern and southern lights. 2. Sunspots are cooler areas on the photosphere that last for about 2 months 3. Solar Flares are violent eruptions or solar particles and radiation 4. Prominences are an arc of gas that is ejected from the chromosphere and rains back to the surface SOLAR FLARE SOLAR PROMINENCE Sunspots Flare Prominence Solar Wind Comets: orbit the sun and consist mostly of frozen gases which vaporize in sunlight forming an atmosphere and sometimes a tail—the tail always points away from the sun. A meteoroid is debris located outside of Earth’s atmosphere that orbits the sun. •A meteor is debris located within Earth’s atmosphere that vaporizes…known as a shooting star. •A meteorite is a meteoroid that survives its passage through Earth’s atmosphere and hits Earth’s surface. Asteroids are usually leftover debris of the formation of the solar system. They orbit the sun between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt which separates the 2 types of planets. AMAZING EARTH SCIENCE FACTS Summer Solstice is June 21st (longest day). 1. ____________ Winter 2. ____________ Solstice is December 21st (shortest day) Equinoxes occur when the sun is directly over the 3. ____________ equator….Spring is March 21st and Fall is September 22nd. (12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of night) 4. The sun is a star that is made up of the 2 gases hydrogen and ________. helium ___________ AU is the distance from the sun to the 5. One _____ earth…93 million miles.