* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CARBON CYCLE - Issaquah Connect
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Iron fertilization wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Carbon pricing in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Carbon capture and storage (timeline) wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sequestration wikipedia , lookup
Climate-friendly gardening wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
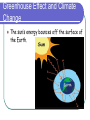
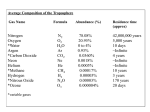
THE CARBON CYCLE-part 3 Carbon Cycle The same carbon atoms are used over and over on earth. They cycle between the earth & the atmosphere. Carbon Storage…Fossil Fuels Some organisms are not decomposed fully & end up in deposits underground (oil, coal, etc… known as fossil fuels). Carbon Storage…Fossil Fuels Carbon is stored in rocks & underground deposits & is released very slowly into the atmosphere. Carbon Storage…Fossil Fuels This process takes many years and is called a carbon sink or carbon store. Fossil Fuels and CO2 When fossil fuels are burned, the carbon in them is released to the atmosphere. Human Impact Burning anything releases more carbon into the atmosphere — especially fossil fuels. Burning Fossil Fuels releases carbon stores Increased carbon dioxide in atmosphere increases the greenhouse effect. Human Impact Scientists think this leads to Global Climate Change. Fewer plants = less CO2 removed from the atmosphere. Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change The sun’s energy bounces off the surface of the Earth. Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change Greenhouse gases form a layer in the atmosphere that traps some of the energy. Examples: Carbon Dioxide and Water (vapor). This warms the Earth. Without this layer, it would be too cold for life as we know it. Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change The more carbon dioxide that is released to the atmosphere, the warmer the earth becomes. Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change This causes changes in different climates around the world. Cycle – Repeats Over and Over and Over and Over … Carbon Cycle Diagram Carbon in Atmosphere Decomposers break down dead things, releasing carbon to atmosphere & soil Fossil fuels are burned; carbon is returned to atmosphere Carbon slowly released from these substances returns to atmosphere Plants use carbon to make food Plants and animals die Bodies not decomposed — after many years, become part of oil or coal deposits (fossil fuels) Animals eat plants and take in carbon Carbon Storage…Oceans Carbon reacts with sea water and is stored in the ocean…this is another Carbon Sink or Carbon Store. Oceans contain earth’s largest store of carbon. Many animals pull carbon from water to make shells, etc. Animals die and carbon substances are deposited at the bottom of the ocean. The Carbon Cycle What can we do to limit climate change? Burn less, especially fossil fuels Promote plant life, especially trees