* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA History Function Structure
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
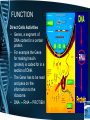
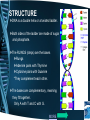
DNA History Function Structure Replication History - Structure Erwin Chargaff – 1950’s Discovered that the amount of A is always equal to the amount of T. – The amount of C is always equal to the amount of G. – What can be inferred? • A goes with T • G goes with C – This became known as Chargaff’s Rule Rosalind Franklin • 1950’s she used x-ray diffraction to take a “photo” of DNA. Watson & Crick •1953 Using their own research and other the created a model of DNA. •DNA described as Double Helix or twisted ladder. FUNCTION Direct Cells Activities • Genes, a segment of DNA codes for a certain protein. • For example the Gene for making Insulin (protein) is coded for in a section of DNA. • The Gene has to be read and pass on the information to the ribosome. • DNA RNA PROTIEN STRUCTURE DNA is a double helix or a twisted ladder. Both sides of the ladder are made of sugar and phosphate. The RUNGS (steps) are the bases Rungs Adenine pairs with Thymine Cytosine pairs with Guanine *They complement each other. The bases are complementary, meaning they fit together. Only A with T and C with G. MORE BUILDING BLOCKS OF DNA. DNA is like a puzzle where only certain pieces of the puzzle fit together. Each puzzle piece is called NUCLEOTIDE. Each puzzle piece is made of a: SUGAR, PHOSPHATE NITROGEN BASE. 4 Bases Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine Replication oPurpose is to make an exact copy of the DNA molecule. o Why? oSo during cell division (mitosis) each new cell has an exact copy of the original. •STEPS OF REPLICATION: 1.Enzyme (polymerase) UNZIPS the DNA at the weak hydrogen bonds. 2.Free floating nucleotides of DNA BOND to the single strand by BASE PAIRING. 3.Another enzyme rezips the two chains together. FINAL PRODUCT A total of 4 strands in groups of two.