* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the course overview
Survey
Document related concepts
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
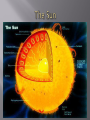
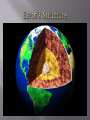
We begin the course with some introductory "sciencey" stuff; such as: Introduction to space and earth science Method of Scientists Review how we carry out scientific investigations. Scientific Notation Communication in Science (laws vs. theories) latitude and longitude and other basic Earth facts. Unit 1: Science of the Universe We will look at a number phenomena of the universe including the big bang theory, galaxies, red shift, star formation, and black holes. In later units we will examine the techniques used to identify and measure such phenomena. In addition, we will analyze major milestones in astronomical theory and developments in astronomical technology. Unit 2: Planetary Science We will investigate the features and interactions between bodies in the solar system and their impact on the existence of life. We examine the following topics: - The formation and composition of the solar system. - Properties of the Earth that protect life from hazards. - Compare Earth with other objects in the solar system. - Identify geological processes common to Earth and other bodies in our solar system. Unit 3: Recording Earth’s Geological History This unit will examine the relationship between climate, geology, and life on Earth through referencing geological records. You will further investigate Earth's geological history in terms of the major changes that have occurred, the processes that caused them, and how such changes are recorded. Some additional topics that will be covered include: - Investigating the geological history of an area of Ontario. Compare geological time scales to human time scales. Causes of changes to Earth's atmospheric conditions over time. Evolution of life. Dating techniques and radioactive decay. Unit 4: Earth Materials This unit will take a look at minerals and their properties in the formation of rocks. You will also examine the properties of such minerals, the technologies used to extract them, and the impact of the exploitation of such materials. Some other topics to be covered are: - The investigation of sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. - The role of Earth materials in the disposal of waste and toxic materials. - Investigation and inquiry of minerals and the factors that determine the size of their crystals. You will also examine the impact on economies of the extraction of various Earth materials. They will also analyze the technologies and techniques used for this extraction, and the possible environmental repercussions. Unit 5: Geological Processes This unit will examine internal and external geological processes on Earth. As well, it will analyze those technologies that allow for our examination of such processes. Some other areas covered include: - Investigation of weathering, erosion, seismic activity, and various land slides and falls. - An examination of lithospheric plates and the major areas of tectonic activity. Students will also assess the reliability of technological methods of monitoring earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. They will also analyze the relationship between human activities and geological structures and processes.