* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
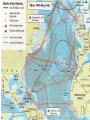
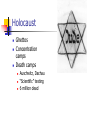
World War II Chapter 14 and 15 Failures of Treaty of Versailles Peace did not bring prosperity Revolution and economic depression Nationalism- pride in country Failures Caused anger and resentment Germany felt they were treated unfairly Soviets upset that part of their land was carved out People turned to authoritarian leaders Joseph Stalin and the Soviet Union Civil War between the Bolsheviks and Mensheviks led to Soviet control. After Lenin dies, fight for control and Joseph Stalin wins. Communist state Agricultural and Economic growth, no privately owned farms- use of collectives Tried to make country an industrial power with his five year plans By 1937, they were number 2 Somewhere between 8-13 million Russians died because of this Totalitarian Government Benito Mussolini in Italy Totalitarian regime Played on the fears of economic collapse and communism in the middle and upper class Fascist Party- stressed nationalism and the interests of the state over the individual Power in the hands of a strong leader and a small number of party officials October 1922 Mussolini marched on Rome with his black shirts and the king made him the head of the government, Il Duce takes power Hitler in Germany National Socialist German Workers’ Party or the NAZI’s, became his party’s leader and called himself Der Fuhrer Jail time wrote Mein Kampf, fascist, extreme nationist. Called for uniting all German speaking people in a great German empire Racial purification National expansion, needed lebensraum, or living space Great Depression helped Nazi’s come to power Hitler’s private army, the brown shirts (storm troopers) January 1933 Hitler pronounced Chancellor and established the Third Reich after dismissing the Weimar Republic Hitler’s Youth Japan Nationalistic military tries to take over country They wanted more living space Launched an attack on Manchuria, part of China in 1931 League of Nations condemned them but did nothing else Militarists in Japan come to power More Aggression In 1933 Hitler pulled out of the League of nations and in 1935 started a build-up of Germany’s army 1936 Hitler took the Rhineland, and the League did nothing Appeasement- giving into demands to avoid a larger conflict Mussolini took Ethiopia, the League boycotted Italy in 1936 Franco and Spain The military under Francisco Franco rebelled against the government. Spanish Civil War 3,000 Americans fought against Franco in the Lincoln Battalion Mussolini and Hitler supported Franco Those two countries form the Rome-Berlin Axis 500,000 dead but Franco wins in 1939 and sets up a Fascist government US Responds Cautiously to Dictators Isolationism Roosevelt promised to stay out of world events Good Neighbor Policy Gave economic aid to Latin America, new trade agreements, respect internal affairs of Latin America, nullified Platt Amendment, withdrew marines from Haiti Soviet Union Neutrality Acts Japan invades China War in Europe Germany then sets its eyes on Austria and easily combines with it because the people support unification in 1937 Hitler looked at Czechoslovakia for more living space and natural resources France and Britain promised to protect Czechoslovakia However, the leaders, Neville Chamberlain and Edouard Daladier wanted to avoid war and since Hitler promised no war, they gave him the Sudentenland in 1938, he takes all of Czechoslovakia in 1939 Poland Hitler wants Poland Signs Non-aggression pact with the Soviet Union which divides Poland Hitler blitzkriegs Poland France and Great Britain declare war on Germany 1939 French and British sit on the Maginot Line and Germany on the Siegfried Line starting the Sitzkrieg April 1940 Hitler attacks Norway, Netherlands, Belgium , and Luxembourg Stalin takes Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Finland France Fall of France- Germans swiftly moved through France trapping 400,000 soldiers at Dunkirk. 330,000 made their way across the channel anyway they could Italy joined the war and also invaded France June 22, 1940 France surrendered, Northern France was controlled by the Nazi’s, and the southern part was the Vichy government under Marshall Philippe Petain. Charles De Gaulle fled to England and set up an exile government- Britain Battle of Britain-air and naval war after defeating France. Luftwaffe bombed British cities all day and night The RAF fought back After six weeks Hitler called the invasion off Bombing of major cities continued America Moves Toward War 1939 Congress passes the Cash-and-Carry provision Neutrality Act of 1939 Tripartite Pact= Axis Powers Build up of US National Defense First peacetime draft 1940 Election Lend-Lease Act Headed Toward War Germany breaks non-aggression pact and invades the Soviet Union We start Lend-Lease agreement with the Soviets German boats start sinking supply ships Wolf packs FDR allowed warships to attack in self-defense 1941 Congress also allowed merchant ships to be armed FDR Prepares Atlantic Charter with Winston Churchill Pledged collective security, disarmament, selfdetermination, economic cooperation, and freedom of the seas Basis of United Nations Japan versus the US Hideki Tojo invaded China Invade Southeast Asia US cuts off trade and begins an embargo on oil Tojo looks to war, promises emperor peace December 7, “a day that will live in infamy” 2403 Americans were killed 1,178 were wounded, 21 ships were sunk or damaged, 300 aircraft were damaged or destroyed Declared War on December 8 War for the United States Battle of the Atlantic Hitler successful at first Convoys By 1943 the tide of the battle had switched to the Allies Battle of Stalingrad German took 9/10 of the city until winter came January 1943 Germany surrenders 1,100,00 Soviets lost their lives Turning point in Europe North Africa Front Opened a second front to get the Germans away from the Soviet Union Operation Torch led by Dwight D. Eisenhower US landed in Casablanca, British started in Egypt Chased the Afrika Korps led by Erwin Rommel May 1943 take back Africa George Patton put in charge of North African forces Invade Italy September 3, 1943 Italy surrendered Mussolini out, Italy changes sides Hitler sent in troops to stop invasion Bloody Anzio Italy not freed until 1945 Germany Allies started bombing Germany in 1942 Saturation bombing- continuous bombing Strategic bombing- destroy Germany’s capacity to make war Tuskegee Airman escorted bombers and protected them Successful, but with high losses. War in the Pacific Japanese spread until they have a bigger empire than Hitler Philippines and MacArthur Doolittle’s Raid-nighttime bombing against Tokyo Battle of Coral Sea- ended Japanese attack on New Guinea, draw, 1942 Battle of Midway- US broke Japanese code and new about planned attack. Admiral Chester Nimitz prepared for attach. Turning point of the war Battle of Guadalcanal- American on the offensive Bataan Death March- 76,000 Americans and Filipinos, 7,000 die 3 months of fighting Battle of Leyte Gulf Kamikaze Response 16 million Americans will serve during the war Army, navy and marines all grew Women’s Army Corps (WAC) provided clerical workers, truck drivers, instructors, and lab technicians for the army 150,000 served, 57,000 nurses served in the Army Nurse Corps War Production Board oversaw the conversion of peace time industry to war industry Allocated scarce materials, regulation production of civilian goods, establish production contracts, negotiate with labor, and control inflation Home Front Jobs!!!! Women in the workforceRosie the Riveter 1/3rd of workforce Jobs outside of traditional ones Industry as well as clerical and secretarial Shift in population Children Daycare centers African Americans Civil Rights Protests Jobs remained segregated “Double V” Campaign Leader A. Phillip Randolph called for victory against fascism and against discrimination at home FDR feared a March on Washington so he issued Executive Order 8802- fair hiring practices for any job funded with government money and established the Fair Employment Practices Committee to enforce it Congress of Racial Equality founded in 1942 to fight segregation with non violent measures NAACP grew in membership Workers on the Move and Restrictions Wartime migration Rural population drain Bracero program brought Mexican laborers to work on farms Detroit race riots Zoot Suit Riots Germans, Italians and Japanese arrested FDR later removed the first two Supporting the War Effort 5% tax on all Americans People bought war bonds Office of Price Administration- authority to control wages and set maximum prices Rationing Office of War Information worked with the media to support the war effort Hollywood got involved Stereotyped the enemy Japanese American Internment 1942 removal of 110,000 Japanese-Americans to internment camps Nisei and Issei Some went to war in Europe Korematsu v. United States Japanese American Citizens League 1965 Ronald Reagan and restitution Liberation of Europe Plan to invade France under General Dwight D. Eisenhower Planned attack at Normandy D-Day, Operation Overlord June 6, 1944 Fake plans to attack Calais Amphibious assault Patton and Bradley advance France is liberated by September 1944 Success in Europe Belgium and Luxembourg Freed 1944 Election year October 1944 troops are in Germany Battle of the Bulge Germans lose April 25, 1945 Soviet troops are in Berlin April 29, Hitler and wife kill themselves while still blaming the Jews Eisenhower accepted unconditional surrender May 8 V-E Day Roosevelt died before the end, April 12, 1945 Iwo Jima and Okinawa Iwo Jima Means sulfur island Critical because had two runways that Japanese used to attack 20,700 Japanese protected it and were underground Also we could use to attack Japan 6,000 Americans died, only 200 Japanese survived Okinawa-April 1945 1900 kamikaze attacks, sank 39 ships, damaged 300 more and killed 5,000 seamen By the end on June 21, 1945 7600 Americans dead and 110,000 Japanese Fear of invading actual Japan Manhattan Project General Leslie Groves and J. Robert Oppenheimer Included 600,000 Americans July 16, 1945 Alamogordo, New Mexico- first bomb detonated Truman’s debate Hiroshima August 6 the Enola Gay Nagasaki August 9 V-J day August 15 September 2, 1945 Japan formally surrenders to MacArthur on the Missouri Holocaust Persecution of Jews Anti-Semitism Kristallnacht Attacked Jewish homes, businesses, synagogues Escape, not likely The Final Solution Others in Hitler’s way Holocaust Ghettos Concentration camps Death camps Auschwitz, Dachau “Scientific” testing 6 million dead