* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
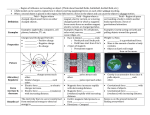
Name:___________________________________ Date:______________ Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Magnetism Directions: write the word or phrase from the word bank in the blank below that correctly describes the idea. Word Bank: Magnetic poles, like, current, magnetic domains, magnetic field lines, magnetism, repel, permanent magnet, opposite, electromagnet, magnetic field, alternating current, direct current, galvanometer 1. ____________________ What the properties of magnets and their interactions are referred to as. 2. ____________________ The regions on a magnet where the magnetic force is strongest. 3. ____________________ Current that flows in only one direction. 4. ____________________ A device that uses an electromagnet to measure electric current. 5. ____________________ The south pole of a magnet will _____ the south pole of another magnet. 6. ____________________ When current in a circuit reverses its direction at regular intervals. 7. ____________________ Groups of aligned atoms in a magnet. 8. ____________________ Formed by placing a piece of iron inside a current carrying coil of wire. 9. ____________________ Type of magnet that keeps its magnetic properties for a long time. 10. ____________________ Type of magnetic poles that attract each other. 11. ____________________ Type of magnetic poles that repel each other. 12. ____________________ The area around magnets affected by their force. 13. ____________________ Are drawn to represent the area of force around a magnet. 14. ____________________ You can increase the strength of an electromagnet by adding ____ to the wire or adding ____ to the wire. Directions: circle the word that correctly completes the idea. 15. A motor converts (electrical, mechanical) energy into (electrical, mechanical) energy. 16. A generator converts (electrical, mechanical) energy into (electrical, mechanical) energy. 17. When (resistance, current) is passed through a coil of wire with a piece of iron inside, an electromagnet is formed. 18. An electromagnet is a (permanent, temporary) magnet. 19. Adding more loops of wire to the coil (increases, decreases) the strength of an electromagnet. 20. More current flowing will (increase, decrease) the strength of an electromagnet. 21. Electromagnets change (chemical, electrical) energy into mechanical energy. 22. An instrument that is used to detect current is (an electromagnet, a galvanometer). 23. A coil’s magnetic field can be flipped by (reversing the direction of current, increasing the number of loops) in the coil. 24. A motor (uses, creates) an electric current as it turns. 25. A generator (uses, creates) an electric current as it turns. 26. The current produced by a generator is (direct, alternating) current.


















![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)

