* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bohr Atom
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
James Franck wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
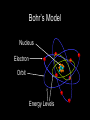
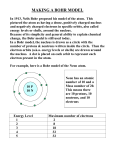
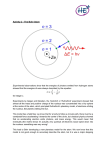
Bohr’s Model Nucleus Electron Orbit Energy Levels Bohr Model of Atom Increasing energy of orbits n=3 e- n=2 e- n=1 ee- e- e- ee- e- e- eA photon is emitted with energy E = hf The Bohr model of the atom, like many ideas in the history of science, was at first prompted by and later partially disproved by experimentation. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Chemistry An unsatisfactory model for the hydrogen atom According to classical physics, light should be emitted as the electron circles the nucleus. A loss of energy would cause the electron to be drawn closer to the nucleus and eventually spiral into it. Hill, Petrucci, General Chemistry An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition, page 294 Quantum Mechanical Model Niels Bohr & Albert Einstein Modern atomic theory describes the electronic structure of the atom as the probability of finding electrons within certain regions of space (orbitals). Modern View • The atom is mostly empty space • Two regions – Nucleus • protons and neutrons – Electron cloud • region where you might find an electron