* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is a cell? - Epiphany Catholic School
Survey
Document related concepts
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
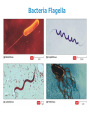
th 7 Science Cells and Heredity (Module A) Unit 1: Cells Lesson 1: Characteristics of Cells Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What is a cell? • A cell is the smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms. • Organism - any living thing that carries out its own life processes. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells Cell size All cells are small - size is limited by their outer surface area. • If too large, can’t take in enough nutrients or get rid of enough wastes. • The surface area-to-volume ratio: ratio of the outer surface to the cell’s volume. • The smaller the cell, the greater this ratio. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells Cell theory Three basic components: 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of all organisms. 3. All cells come from existing cells. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson Characteristics of Cells Cell Hall 1ofTheFame •Robert Hooke (1665) - first to describe cells. He looked at the bark of a cork tree under a microscope (that he built). • Thought that cork cells looked like cells in monastery Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells Cell Hall of Fame (con’t) read pg. 8-9 • Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1673) made first microscope, described “wee beasties” in pond water. • Matthias Schleiden (1838) said all plants are made of cells. • Theodor Schwann (1839) said all animals tissues are made of cells. • Rudolf Virchow (1858) said cells divide to form new cells Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells A few more important cell theory things: • Unicellular organisms: Organisms made up of just one cell • One cell has to carry out ALL life functions. • multicellular organisms: Organisms made up of more than one cell • Cells have specialized functions. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 Theof Characteristics Two types cells of Cells • Prokaryotes - No nucleus or membrane-bound organelles • All are single-celled • DNA is in the cytoplasm • Have ribosomes to make proteins • Some have flagella to help move • Smaller than eukaryotes • Examples: bacteria, archaea Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Bacteria Flagella Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells • Eukaryotes - have DNA in a nucleus • Have other membrane-bound organelles • Most are multicellular • Also have ribosomes (not membrane bound) • Examples: animals, plants, protists, fungi • Do page 11 Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells All cells have… • cell membrane – protective outer layer • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material that provides instructions for all cell processes Do page 10 Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What parts do all cells have in common? • How many parts of a cell can you name? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company