* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 History and Approaches 2017
Survey
Document related concepts
Peace psychology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Psychologist wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Index of psychology articles wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Trans-species psychology wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
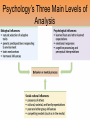
Unit 1: History and Approaches • Psychology is a scientific study of mental processes and behaviors. Prescientific Psychology • Ancient Greeks –Socrates –Plato –Aristotle Prescientific Psychology • Rene Descartes • Francis Bacon • John Locke –Tabula Rasa (blank slate) • Empiricism Empiricism = the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation. Lets make this easy….its SCIENCE Psychological Science is Born • Wilhelm Wundt (Father of Psychology) –University of Leipzig (1st psych lab) –Reaction time experiment Structuralism = an early school of psychology that used introspection to explore the structural elements of the human mind. • Edward Titchener –Structuralism • Introspection – Everything you sense Functionalism = a school of psychology that focused on how our mental and behavioral processes function – how they enable us to adapt, survive, and flourish. • William James –Wrote 1st Psychology Textbook -Functionalism Mary Calkins • Screwed out of her degree –Margaret Floy Washburn • 1st Woman to receive Ph.D. Experimental Psychology = the study of behavior and thinking using the experimental method. Gestalt Psychology • a movement in psychology founded in Germany, trying to explain perceptions in terms of whole parts rather than by analyzing their small parts • The whole is greater than the sum of its parts • Max Wetheimer Psychoanalysis • Sigmund Freud Freud belived • Unconscious mind – what we are not aware of • Repress bad memories – Repression • Dreams tell us about our unconsciousness – Dream Analysis • Defense mechanisms – – We use these as a way to deal with things that bother us Behaviorism = the view that psychology studies behavior without reference to mental processes. Study of observable behavior –Ivan Pavlov –John B. Watson –B.F. Skinner Humanistic Psychology = emphasized the growth potential of healthy people and the individual’s potential for personal growth. • Humanistic psychology –Carl Rogers –Abraham Maslow Cognitive Perspective = study of cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language). Psychoanalytic Psychology = studies how unconscious drives and conflicts influence behavior, and uses that information to treat people with psychological disorders. Biological/Neuroscience Psychology = a branch of psychology that studies the links between biological (including neuroscience and behavior genetics) and psychological processes. Evolutionary Psychology = the study of the roots of behavior and mental processes using the principles of natural selection. Behavioral Psychology = the scientific study of observable behavior, and its explanation by principles of learning. Cognitive Perspective = study of cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language). Social-Cultural Psychology = the study of how situations and cultures affect our behavior and thinking. Psychological Approaches/Perspectives Psychological Approaches/Perspectives Psychology’s Three Main Levels of Analysis –Biological factors –Psychological factors –Social-cultural factors All guide behavior • Biopsychosocial Approach Psychology’s Three Main Levels of Analysis