* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
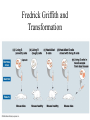
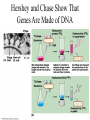
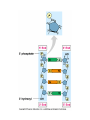
DNA The Genetic Material QUESTION Is the structure and function of DNA the same in almost all organisms? Fredrick Griffith and Transformation Hershey and Chase Show That Genes Are Made of DNA Structure of DNA Nucleotides Are the Building Blocks. • There are three components to a nucleotide – Sugar (5 carbon) – Nitrogenous base (adenine, quanine, thymine, cytosine) – Phosphate group Semi-conservative Model of DNA Replication • Prokayotes – One circular chromosome – 5 million base pairs – Replicates in less than one hour • Eukaryotes – Humans have 46 chromosomes – 6 billion base pairs – Replicated in a few hours – DNA is separated from most of the replication machinery by the nuclear envelop. Both carry out replication very quickly and with tremendous accuracy – 1 error /billion nucleotides. The Bases Are Either Purines or Pyrimidines. A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G. This is because of the number of bonds formed between the bases. Two hydrogen bonds form between A and T and three between C and G. Write the compliment for GGCTATTGGCA. DNA Replication • Steps in replication – DNA helix is unwound by helicase. – The point where the DNA strands separate is called the replication fork (Y) – At the replication fork, the enzyme DNA polymerase adds bases according to the basepairing rules. – Two new DNA helixes are formed. Replication Begins at the Origin of Replication • Prokaryotes have only one (1) origin of replication. • Eukaryotes have 100’s or 1000’s of origins of replications. • Replication proceeds in both directions, forming a replication bubble. • At the ends of the replication bubble is the replication fork – a” Y shaped” region. • DNA polymerase has the ability to proofread and make corrections if an error has been made. After proofreading the rate of errors is one per billion nucleotides. • There are multiple DNA replication forks in a strand of linear DNA creating replicating “bubbles.” (Without multiple replication forks, it would take 16 days to copy one DNA molecule.) What Is the Energy Source for Replication? • The energy source is a nucleoside triphosphate. • This molecule is similar to ATP except the sugar is deoxyribose and the sugar in ATP is ribose. • The energy comes from the hydrolysis of the phosphate tail. DNA Is Anti-parallel Structure of A Gene • Genes are DNA –encoded information that specifies particular proteins; each gene is made of a specific sequence of nucleotides. • Genes are composed of coding and noncoding sequences. – Coding sequences are exons (code for amino acids) – Noncoding sequences are introns (intervening) Telomeres • Telomeres are special nucleotide sequences located at the end of chromosomes. • They do not contain genes but mutliple repetitions of short nucleotide sequences (100-1000) • Telomerase When the introns are removed, the resulting fragments are stitched together to make a protein.