* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Components of the Marketing Plan
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
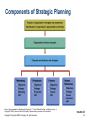
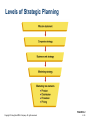
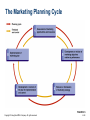
Part One Marketing and Its Environment 2 Strategic Planning Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook Chapter Learning Objectives • To describe the strategic planning process • To explain how organizational resources and opportunities affect the planning process • To understand the role of the mission statement in strategic planning • To examine corporate, business-unit, and marketing strategies • To understand the process of creating the marketing plan Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–2 Chapter Outline • Understanding the Strategic Planning Process • Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities • Establishing an Organizational Mission and Goals • Developing Corporate and Business-Unit Strategies • Developing a Marketing Strategy • Creating the Marketing Plan Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–3 Understanding the Strategic Planning Process • Strategic Planning –The process of establishing an organizational mission and formulating goals, corporate strategy, marketing objectives, marketing strategy, and a marketing plan Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–4 Components of Strategic Planning Source: Figure adapted from Marketing Strategy by O. C. Ferrell, Michael Hartline, and George Lucas, Jr. Copyright © 2002 by Harcourt Brace & Company. Reproduced by permission of the publisher. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 2.1 2–5 Understanding the Strategic Planning Process (cont’d) • Marketing Strategy –A strategy for identifying and analyzing a target market and developing a marketing mix to meet the needs of that market • Marketing Plan –A written document that specifies the activities to be performed to implement and control an organization’s marketing activities Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–6 Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities • Core Competencies –Things a firm does extremely well (strengths), which sometimes give it an advantage over its competition • Financial and human resources • Reputation, goodwill, and brand names Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–7 Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities (cont’d) • Market Opportunity –A combination of circumstances and timing that permits an organization to reach a target market • Core competencies are matched to opportunities • Strategic windows—temporary periods of optimal fit between the key requirements of a market and the particular capabilities of a firm Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–8 Assessing Organizational Resources and Opportunities (cont’d) • Competitive Advantage –The result of a company’s matching a core competency (superior skill or resources) to opportunities in the marketplace • Manufacturing skills • Technical skills • Marketing skills Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–9 Establishing an Organizational Mission and Goals • Mission Statement –A long-term view, or vision, of what the organization wants to become –Mission statement answers two questions: • Who are our customers? • What is our core competency? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–10 Establishing an Organizational Mission and Goals (cont’d) • Mission Statement Benefits –Provides a clear purpose and direction that keeps the organization on track –Distinguishes the organization from competing organizations –Provides direction for strategic planning –Fosters a marketing orientation Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–11 Southwest Airlines Mission Statement Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–12 Establishing an Organizational Mission and Goals (cont’d) • Organizational goals –are derived from the mission statement. –provide focus for the end results (attainment of goals) the organization seeks. • Short-term goals addressing immediate competitive necessities • Long-term goals for achieving sustainable competitive advantage Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–13 Developing Corporate and Business-Unit Strategies • Corporate Strategy –A strategy that determines the means for utilizing resources in the various functional areas to reach the organization’s goals • • • • Determines the scope of the business Guides its resource deployment Identifies its competitive advantages Provides overall coordination of functional areas Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–14 Developing Corporate and Business-Unit Strategies (cont’d) • Issues Impacting on Corporate Strategy Development –Corporate culture –Competition –Differentiation –Diversification –Interrelationships among business units –Environment concerns and social issues Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–15 Levels of Strategic Planning FIGURE 2.2 Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–16 Business-Unit Strategy • Strategic Business Unit (SBU) –A division, product line, or other profit center within a parent company • Portfolio Analysis –Classification of the individual performance capabilities of each of the SBUs in the firm’s portfolio to determine the proper allocation of scarce resources among those divisions Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–17 Business-Unit Strategy (cont’d) • Market –A group of individuals and/or organizations that have needs for products in a product class and have the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase those products • Market Share –The percentage of a market that actually buys a specific product from a particular company Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–18 Business-Unit Strategy (cont’d) • Market-Growth/Market-Share Matrix –A strategic planning tool based on the philosophy that a product’s market growth rate and market share are important in determining marketing strategy –Factors determining SBU/product’s position within a matrix • Product-market growth rate • Relative market share Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–19 Growth-Share Matrix Developed by the Boston Consulting Group Source: Perspectives, No. 66, “The Product Portfolio.” Reprinted by permission from The Boston Consulting Group, Inc., Boston, MA. Copyright © 1970. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 2.3 2–20 Business-Unit Strategy (cont’d) • Market-Growth/Market-Share Matrix (cont’d) –BCG Classification • Star—high growth market, dominant market share –requires additional resources for continued growth • Cash cow—low growth, dominant market share –generates surplus resources for allocation to other SBUs • Dog—low/declining market, subordinate market share –has diminished prospects and represents a drain on the portfolio • Question mark—high growth market, low market share –represents a high-risk/cost opportunity requiring a large commitment of resources to build market share Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–21 Growth Strategies for Business Units • Intensive Growth –Growth occurring when current products and current markets have the potential for increasing sales –Market penetration: increasing sales of current products in current markets –Market development: increasing sales of current product in new markets –Product development: increasing sales by improving present products or developing new products for current markets Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–22 Growth Strategies for Business Units (cont’d) • Diversified Growth –Growth occurring when new products are developed to be sold in new markets –Advantage of diversified growth is the spread of risk across a number of markets –Diversification allows for a wider use of managerial, technical, and financial resources Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–23 Competitive Growth Strategies Source: H. I. Ansoff, New Corporate Strategy (New York: Wiley, 1988), p. 109. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 2.4 2–24 Developing a Marketing Strategy • Target Market Selection –Defining/understanding the target market by • focusing on specific profitable customer groups/market segments. • recognizing changes occurring in the market. • Creating the Marketing Mix • Analyze customer needs, preferences, and behavior • Have the skills and resources required for product design, pricing, distribution, and promotion • Maintain strategic consistency and flexibility in marketing mix decisions Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–25 Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–26 Creating the Marketing Plan • Marketing Planning –The process of assessing opportunities and resources, determining objectives, defining strategies, and establishing guidelines for implementation and control of the marketing program –Planning time periods • Short-range: one year or less • Moderate-range: one to five years • Long-range: more that five years Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–27 The Marketing Planning Cycle FIGURE 2.5 Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–28 The Marketing Planning Cycle (cont’d) 1. Assessment of marketing opportunities and resources 2. Development or revision of marketing objectives relative to performance 3. Revision or formulation of marketing strategy 4. Development or revision of the plan for implementation and control 5. Implementation of marketing plan Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–29 The Marketing Planning Cycle (cont’d) • Benefits of Planning –Provides the basis for internal communication among employees –Defines the assignment of responsibilities and tasks and sets the schedules for implementation –Presents objectives and specifies resource allocations –Helps in monitoring and evaluating the performance of the marketing strategy Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–30 Components of the Marketing Plan • Executive Summary –A synopsis of the the entire marketing plan • Introduction, major plan aspects, implementation costs • Environmental Analysis –Marketing environment • Competitive, economic, political, legal and regulatory, technological, and sociocultural factors –Target market(s) • Current and anticipated market/customer needs –Current marketing objectives and performance • Consistency of objectives with marketing environment Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–31 Components of the Marketing Plan (cont’d) • SWOT Analysis –An assessment of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats • • • • Strengths—competitive advantages or core competencies Weaknesses—limitations on competitive capability Opportunities—favorable conditions in the environment Threats—conditions or barriers to reaching objectives Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–32 The Four-Cell SWOT Matrix Source: Adapted from Nigel F. Piercy, Market-Led Strategic Change. Copyright © 1992 Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd., p. 371. Used with permission. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 2.6 2–33 Components of the Marketing Plan (cont’d) • Marketing Objectives –A statement of what is to be accomplished through marketing activities that match strengths to opportunities, and provide for the conversion of weaknesses to strengths • • • • Stated in clear, simple terms Should be accurately measurable Specify a time frame for accomplishment Consistent with business-unit and corporate strategy Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–34 Components of the Marketing Plan (cont’d) • Marketing Strategies –A description of how the firm will achieve its marketing objectives and manage its relationship with its customers to gain advantage over the competition • Choice of target market • Development of the marketing mix –Sustainable competitive advantage • An advantage that the competition cannot copy that is the intended result of the successful implementation of the marketing plan Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–35 Components of the Marketing Plan (cont’d) • Marketing Implementation –Specific actions and activities that will be taken to carry out the marketing strategy • Activities, responsibilities, costs, schedules/timetables • Evaluation and Control –Defines how the success of the plan will be measured • Sets performance standards and variance correction measures • Financial monitoring procedures and controls (audits) Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–36 Components of the Marketing Plan (cont’d) • Using the Marketing Plan –Putting effort and creative thought into the plan is essential. –Having a good marketing information system is critical. –Exercising sound managerial judgment is necessary. –Following the plan while maintaining adaptive flexibility in adjusting to changing market environment conditions is required. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–37 After reviewing this chapter you should: • Be able to describe the strategic planning process. • Know how organizational resources and opportunities affect the planning process. • Understand the role of the mission statement in strategic planning. • Be familiar with corporate, business-unit, and marketing strategies. • Understand the process of creating a marketing plan. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–38 Chapter 2 Supplemental Slides Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–39 Key Terms and Concepts • The following slides (a listing of terms and concepts) are intended for use at the instructor’s discretion. • To rearrange the slide order or alter the content of the presentation –select “Slide Sorter” under View on the main menu. –left click on an individual slide to select it; hold and drag the slide to a new position in the slide show. –To delete an individual slide, click on the slide to select, and press the Delete key. –Select “Normal” under View on the main menu to return to normal view. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–40 Important Terms • Strategic Planning –The process of establishing an organizational mission and formulating goals, corporate strategy, marketing objectives, marketing strategy, and a marketing plan • Marketing Strategy –A strategy for identifying and analyzing a target market and developing a marketing mix to meet the needs of that market • Marketing Plan –A written document that specifies the activities to be performed to implement and control an organization’s marketing activities Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–41 Important Terms • Core Competencies –Things a firm does extremely well (strengths), which sometimes give it an advantage over its competition • Market Opportunity –A combination of circumstances and timing that permits an organization to reach a target market • Strategic Window –A temporary period of optimal fit between the key requirements of a market and the particular capabilities of a firm Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–42 Important Terms • Competitive Advantage –The result of a company’s matching a core competency (superior skill or resources) to opportunities in the marketplace • Mission Statement –A long-term view, or vision, of what the organization wants to become • Corporate Strategy –A strategy that determines the means for utilizing resources in the various functional areas to reach the organization’s goals Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–43 Important Terms • Strategic Business Unit (SBU) –A division, product line, or other profit center within a parent company • Market –A group of individuals and/or organizations that have needs for products in a product class and have the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase these products • Market Share –The percentage of a market that actually buys a specific product from a particular company Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–44 Important Terms • Market-Growth/Market-Share Matrix –A strategic planning tool based on the philosophy that a product’s market growth rate and market share are important in determining marketing strategy • Intensive Growth –Growth occurring when current products and current markets have the potential for increasing sales • Diversified Growth –Growth occurring when new products are developed to be sold in new markets Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–45 Important Terms • Marketing Planning –The process of assessing opportunities and resources, determining objectives, defining strategies, and establishing guidelines for implementation and control of the marketing program • SWOT Analysis –An assessment of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–46 Important Terms • Strengths –Competitive advantages or core competencies that give a firm an advantage in meeting the needs of its target market • Weaknesses –Any limitations a firm faces in developing or implementing a marketing strategy • Opportunities –Favorable conditions in the environment that could produce rewards for an organization if acted on properly Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–47 Important Terms • Threats –Conditions or barriers that may prevent a firm from reaching its objectives • Marketing Objective –A statement of what is to be accomplished through marketing activities • Sustainable Competitive Advantage –An advantage that the competition cannot copy Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–48 Transparency Figure 2D Most Important Role of a Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Source: American Demographics, July 2000, p. 24. Adapted with permission Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2–49