* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 投影片 1
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Sound level meter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
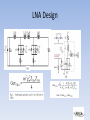
An Ultra-low Voltage UWB CMOS Low Noise Amplifier Yueh-Hua Yu, Yi-Jan Emery Chen, and Deukhyoun Heo* Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan Presenter: Chun-Han Hou ( 侯 鈞 瀚) 1 Abstract 1.This paper presents an ultra-low voltage UWB LNA in a commercial 0.18μm CMOS technology 2. The technique of inductive degeneration is used in a two-stage conventional distributed amplifier to achieve broadband and low noise. 3. The common source single-stage amplifier is cascaded to the conventional distributed amplifier to improve the gain at high frequency. 4. The measured a.gain of the integrated LNA is 10dB b.3dB bandwidth from 2.7 to 9.1 GHz c. average noise figure is 4.65dB d.the IIP3 is 0dBm e.Operated at 0.6V f. The UWB CMOS LNA consumes 7mW 2 Outline 1.Introduction 2.LNA Design 3.Noise Reduction 4.Measurement Result 5.Conclusion 3 Introduction 4 LNA Design The integrated UWB CMOS LNA is composed of a two stage conventional distributed amplifier (CDA) and a common-source single-stage amplifier (CSSA) in cascade. 5 LNA Design 6 Noise Reduction 1.Inductive degeneration is the technique widely used in the tuned LNA design. 2. This technique is applied to the design of every stage of the CDA. 3.Adding source-degeneration inductor improves the noise characteristic of the single stage in the CDA. 7 Measurements 8 Measurements Ps. . The integrated LNA achieves 10dB gain for 3dB bandwidth from 2.7GHz to 9.1GHz. 9 Measurements 10 Measurements Ps.Distributed amplifiers usually have good input and output return losses 11 Measurements [2]A.Bevilacqua and A.Niknejad, “An Ultra-Wideband CMOS LNA for 3.1 to 10.6GHz Wireless Receivers,” ISSCC Dig. Tech. Papers, vol. 1, pp. 384 – 385, Feb. 2004. [6]Chang-Wan Kim, et al., “An ultra-wideband CMOS low noise amplifier for 3-5-GHz UWB system,” Journal of solid state of circuit, vol. 40, pp. 544-547, Feb. 2005. 12 Conclusion 1. An ultra-low voltage UWB LNA was developed in a commercial 0.18μm CMOS technology. 2.Inductor degeneration technique is applied to the conventional distributed amplifier design for the first time to improve broadband noise characteristic. 3. A common-source single-stage amplifier is cascaded to the CDA to improve the gain for low voltage operation. 4. The integrated LNA achieves 10dB gain and 4.65dB average noise figure for the 3-dB bandwidth from 2.7GHz to 9.1GHz. 5. Operated with a 0.6V power supply, the UWB CMOS LNA consumes only 7 mW. 13