* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution notes 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Peppered moth evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
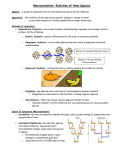
Evolution – change in gene frequency in a population over time (through natural selection) Natural selection Variation among offspring Too many offspring CHANGES IN Competition ENVIRONMENT for resources different rates of survival and reproduction Pepper moths Light trees – light moths most common After industrial revolution Dark trees – dark moths most common 1990’s factories shut down Light trees – return to light moths common Species – type of organism that can only mate with similar organisms to make viable fertile offspring (AP book 474-5) - Prezygotic barrier Geographic isolation Temporal (time) isolation Behavioral isolation -Postzygotic barrier Reduced hybrid viability Fertility Breakdown Sympatric speciation (shared space) In same place – behavioral isolation Temporal isolation (season, time of day) Allopatric speciation Geographic speciation – separated by physical barrier Small populations Genetic drift – gene frequency changes faster by random chance Examples: Founder effect – small #s’ found a new population Bottleneck effect – decrease in genes due to natural disaster Cladogram – branching diagram showing evolutionary relationships, where more close together = more recent Molecular clock – unique mutations occur at fixed intervals (time), therefore can be used to calculate rate of evolution